Non-metric Similarity Graphs for Maximum Inner Product Search
基于非度量相似图的极大内积搜索
Stanislav Morozov Yandex, Lomonosov Moscow State University stanis-morozov@yandex.ru
Stanislav Morozov Yandex, 莫斯科国立大学 stanis-morozov@yandex.ru
Abstract
摘要
In this paper we address the problem of Maximum Inner Product Search (MIPS) that is currently the computational bottleneck in a large number of machine learning applications. While being similar to the nearest neighbor search (NNS), the MIPS problem was shown to be more challenging, as the inner product is not a proper metric function. We propose to solve the MIPS problem with the usage of similarity graphs, i.e., graphs where each vertex is connected to the vertices that are the most similar in terms of some similarity function. Originally, the framework of similarity graphs was proposed for metric spaces and in this paper we naturally extend it to the non-metric MIPS scenario. We demonstrate that, unlike existing approaches, similarity graphs do not require any data transformation to reduce MIPS to the NNS problem and should be used for the original data. Moreover, we explain why such a reduction is detrimental for similarity graphs. By an extensive comparison to the existing approaches, we show that the proposed method is a game-changer in terms of the runtime/accuracy trade-off for the MIPS problem.
本文研究了最大内积搜索(MIPS)问题,该问题目前是众多机器学习应用中的计算瓶颈。虽然与最近邻搜索(NNS)类似,但MIPS问题被证明更具挑战性,因为内积并非严格意义上的度量函数。我们提出利用相似图(similarity graphs)来解决MIPS问题,这种图的每个顶点都与在某种相似度函数下最相似的顶点相连。相似图框架最初是为度量空间设计的,本文将其自然扩展到非度量的MIPS场景。我们证明,与现有方法不同,相似图不需要任何数据转换来将MIPS降维为NNS问题,而应直接用于原始数据。此外,我们解释了这种降维为何会对相似图产生不利影响。通过与现有方法的广泛对比,我们表明所提方法在MIPS问题的运行时间/精度权衡方面具有颠覆性优势。
1 Introduction
1 引言
The Maximum Inner Product Search (MIPS) problem has recently received increased attention from different research communities. The machine learning community has been especially active on this subject, as MIPS arises in a number of important machine learning tasks such as efficient Bayesian inference[1, 2], memory networks training[3], dialog agents[4], reinforcement learning[5]. The MIPS problem formulates as follows. Given the large database of vectors $X={x_{i}\in\mathbb{R}^{\breve{d}}|i=1,\ldots,n}$ and a query vector $q\in\mathbb{R}^{d}$ , we need to find an index $j$ such that
最大内积搜索 (Maximum Inner Product Search, MIPS) 问题近年来受到不同研究领域的广泛关注。机器学习社区对此尤为活跃,因为 MIPS 在多项重要机器学习任务中都有应用,例如高效贝叶斯推理 [1, 2]、记忆网络训练 [3]、对话智能体 [4]、强化学习 [5]。MIPS 问题的定义如下:给定大型向量数据库 $X={x_{i}\in\mathbb{R}^{\breve{d}}|i=1,\ldots,n}$ 和查询向量 $q\in\mathbb{R}^{d}$,我们需要找到一个索引 $j$ 使得
$$
\langle x_{j},q\rangle\geq\langle x_{i},q\rangle=x_{i}^{T}q,i\neq j
$$
$$
\langle x_{j},q\rangle\geq\langle x_{i},q\rangle=x_{i}^{T}q,i\neq j
$$
In practice we often need $K>1$ vectors that provide the largest inner products and the top $K$ MIPS problem is considered.
实践中我们通常需要 $K>1$ 个能提供最大内积的向量,此时考虑的就是前 $K$ 大内积搜索(MIPS)问题。
For large-scale databases the sequential scan with the $O(n d)$ complexity is not feasible, and the efficient approximate methods are required. The current studies on efficient MIPS can be roughly divided into two groups. The methods from the first group [6, 7, 8], which are probably the more popular in the machine learning community, reduce MIPS to the NNS problem. They typically transform the database and query vectors and then search the neighbors via traditional NNS structures, e.g., LSH[7] or partition trees[6]. The second group includes the methods that filter out the unpromising database vectors based on inner product upper bounds, like the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality[9, 10].
对于大规模数据库而言,具有 $O(n d)$ 复杂度的顺序扫描不可行,需要高效的近似方法。当前关于高效MIPS的研究大致可分为两类:第一类方法[6,7,8](在机器学习领域可能更流行)将MIPS转化为NNS问题,通常通过转换数据库和查询向量,再利用传统NNS结构(如LSH[7]或分区树[6])进行近邻搜索;第二类方法则基于内积上界(如柯西-施瓦茨不等式[9,10])过滤掉不具潜力的数据库向量。
In this work we introduce a new research direction for the MIPS problem. We propose to employ the similarity graphs framework that was recently shown to provide the exceptional performance for the nearest neighbor search. In this framework the database is represented as a graph, where each vertex corresponds to a database vector. If two vertices $i$ and $j$ are connected by an edge that means that the corresponding database vectors $x_{i}$ and $x_{j}$ are close in terms of some metric function. The neighbor search for a query $q$ is performed via graph exploration: on each search step, the query moves from the current vertex to one of adjacent vertex, corresponding to a vector, which is the closest to the query. The search terminates when the query reaches a local minimum. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first who expands similarity graphs on the MIPS territory with non-metric similarity function. We summarize the main contributions of this paper below:
在本工作中,我们为MIPS问题引入了一个新的研究方向。我们提出采用最近在最近邻搜索中展现出卓越性能的相似图(similarity graphs)框架。该框架将数据库表示为图结构,其中每个顶点对应一个数据库向量。若两个顶点$i$和$j$通过边相连,则意味着对应的数据库向量$x_{i}$和$x_{j}$在某种度量函数下是相近的。针对查询$q$的邻居搜索通过图遍历实现:在每一步搜索中,查询从当前顶点移动到相邻顶点,该顶点对应的向量与查询最接近。当查询到达局部最小值时,搜索终止。据我们所知,我们是首个将相似图框架扩展到使用非度量相似函数的MIPS领域的研究。本文的主要贡献总结如下:
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: in Section 2, we shortly review the existing MIPS methods and the similarity graphs framework. In Section 3 we advocate the usage of similarity graphs for MIPS and describe the efficient algorithm as well. In addition, we demonstrate that one should not reduce MIPS to NNS when using similarity graphs. In Section 4, we compare the proposed approach to the current state-of-the-art and demonstrate its exceptional advantage over existing methods. Finally, in Section 5 we conclude the paper and summarize the results.
本文其余部分结构如下:第2节简要回顾现有MIPS方法和相似图框架。第3节主张将相似图应用于MIPS问题,并描述高效算法,同时论证在使用相似图时不应将MIPS问题降维为NNS问题。第4节将所提方法与当前最优方法进行对比,展示其超越现有方法的显著优势。最后,第5节总结全文并概括研究成果。
2 Related work
2 相关工作
Now we describe several methods and ideas from the previous research that are essential for description of our method. Hereafter we denote the database by $X={x_{i}\in\mathbb{R}^{d}|i=1,\dots,n}$ and a query vector by $q\in\mathbb{R}^{d}$ .
现在我们介绍几种来自先前研究的方法和思想,这些对于描述我们的方法至关重要。下文将数据库记为 $X={x_{i}\in\mathbb{R}^{d}|i=1,\dots,n}$,查询向量记为 $q\in\mathbb{R}^{d}$。
2.1 The existing approaches to the MIPS problem
2.1 现有解决 MIPS 问题的方法
Reduction to NNS. The first group of methods[6, 7, 8] reformulates the MIPS problem as a NNS problem. Such reformulation becomes possible via mapping the original data to a higher dimensional space. For example, [7] maps a database vector $x$ to
约简为最近邻搜索(NNS)。第一类方法[6, 7, 8]将最大内积搜索(MIPS)问题重新表述为最近邻搜索问题。这种重构通过对原始数据进行高维空间映射实现。例如[7]将数据库向量$x$映射到
$$
\hat{x}=(x,\sqrt{1-|x|^{2}})^{T}
$$
$$
\hat{x}=(x,\sqrt{1-|x|^{2}})^{T}
$$
and a query vector $q$ is mapped to
查询向量 $q$ 被映射到
$$
\boldsymbol{\hat{q}}=(q,0)^{T}
$$
$$
\boldsymbol{\hat{q}}=(q,0)^{T}
$$
The transformation from [7] assumes without loss of generality that $|x|\leq1$ for all $x\in X$ and $|q|=1$ for a query vector $q$ . After the mapping the transformed vectors $\hat{x}$ and $\hat{q}$ have unit norms and
从[7]的转换假设不失一般性,对于所有$x\in X$有$|x|\leq1$,且查询向量$q$满足$|q|=1$。映射后,变换后的向量$\hat{x}$和$\hat{q}$具有单位范数。
$$
|{\hat{x}}-{\hat{q}}|^{2}=|{\hat{x}}|^{2}+|{\hat{q}}|^{2}-2\langle{\hat{x}},{\hat{q}}\rangle=-2\langle x,q\rangle+2
$$
$$
|{\hat{x}}-{\hat{q}}|^{2}=|{\hat{x}}|^{2}+|{\hat{q}}|^{2}-2\langle{\hat{x}},{\hat{q}}\rangle=-2\langle x,q\rangle+2
$$
so the minimization of $\Vert\hat{x}-\hat{q}\Vert$ is equivalent to the maximization of $\langle x,q\rangle$ . Other MIPS-to-NNS transformations are also possible, as shown in [11] and [12], and the empirical comparison of different transformations was recently performed in [6]. After transforming the original data, the MIPS problem becomes equivalent to metric neighbor search and can be solved with standard NNS techniques, like LSH[7], Randomized Partitioning Tree[6] or clustering[8].
因此,最小化 $\Vert\hat{x}-\hat{q}\Vert$ 等价于最大化 $\langle x,q\rangle$。其他 MIPS (Maximum Inner Product Search) 到 NNS (Nearest Neighbor Search) 的转换方法也是可行的,如 [11] 和 [12] 所示,而不同转换方法的实证比较最近在 [6] 中进行了研究。在转换原始数据后,MIPS 问题就等价于度量邻域搜索,并可以使用标准的 NNS 技术来解决,例如 LSH (Locality-Sensitive Hashing) [7]、随机划分树 [6] 或聚类 [8]。
Upper-bounding. Another family of methods use inner product upper bounds to construct a small set of promising candidates, which are then checked exhaustively. For example, the LEMP framework[9] filters out the unpromising database vectors based on the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality. Furthermore, [9] proposes an incremental pruning technique that refines the upper bound by computing the partial inner product over the first several dimensions. The FEXIPRO method[10] goes further and performs SVD over the database vectors to make the first dimensions more meaningful. These steps typically improve the upper bounds, and the incremental pruning becomes more efficient. The very recent
上界法。另一类方法利用内积上界构建少量候选集,再通过穷举验证。例如LEMP框架[9]基于柯西-施瓦茨不等式筛选低潜力数据库向量,并提出增量剪枝技术,通过计算前若干维度的部分内积来优化上界。FEXIPRO方法[10]进一步对数据库向量进行奇异值分解(SVD),使前几个维度更具区分度。这些步骤通常能提升上界质量,使增量剪枝更高效。最新研究...
Greedy-MIPS method[13] uses another upper bound $\langle q,x\rangle=\sum_{i=1}^{d}q_{i}x_{i}\leq d\operatorname*{max}_ {i}{q_{i}x_{i}}$ to construct the candidate set efficiently. The efficiency of upper-bound methods is confirmed by experimental comparison[9, 13] and their source code, available online.
贪婪MIPS方法[13]利用另一个上界 $\langle q,x\rangle=\sum_{i=1}^{d}q_{i}x_{i}\leq d\operatorname*{max}_ {i}{q_{i}x_{i}}$ 来高效构建候选集。实验对比[9, 13]及其在线可获取的源代码证实了这类上界方法的效率。
Despite a large number of existing MIPS methods, the problem is far from being solved, especially given rapidly growing databases in nowadays applications. In this work we propose to solve MIPS with the similarity graphs framework that does not fall into either of the two groups above.
尽管已有大量MIPS方法,但该问题远未解决,尤其是在当今应用数据库快速增长的情况下。本工作中,我们提出利用不属于上述任一分类的相似图框架来解决MIPS问题。
2.2 NNS via similarity graph exploration
2.2 基于相似图探索的最近邻搜索
Here we shortly describe the similarity graphs that are currently used for NNS in metric spaces. For a database $X={x_{i}\in\mathbb{R}^{d}|i=1,\dots,\overset{\cdot}{n}}$ the similarity (or knn-)graph is a graph where each vertex corresponds to one of the database vectors $x$ . The vertices $i$ and $j$ are connected by an edge if $x_{j}$ belongs to the set of $\mathrm{k\Omega}$ nearest neigbors of $x_{i}$ , $x_{j}\in N N_{k}(x_{i})$ in terms of some metric similarity function $s(x,y)$ . The usage of knn-graphs for NNS was initially proposed in the seminal work[14]. The approach[14] constructs the database knn-graph and then performs the search by greedy walk on this graph. First, the search process starts from a random vertex and then on each step a query moves from the current vertex to its neighbor, which appears to be the closest to a query. The process terminates when the query reaches a local minimum. The pseudocode of the greedy walk procedure is presented on Algorithm 1.
这里我们简要描述当前用于度量空间最近邻搜索(NNS)的相似图。对于一个数据库 $X={x_{i}\in\mathbb{R}^{d}|i=1,\dots,\overset{\cdot}{n}}$ ,相似图(或称knn图)是一种每个顶点对应一个数据库向量 $x$ 的图结构。当 $x_{j}$ 属于 $x_{i}$ 的 $\mathrm{k\Omega}$ 最近邻集合 $x_{j}\in N N_{k}(x_{i})$ 时,顶点 $i$ 和 $j$ 会通过边连接,连接依据是某个度量相似函数 $s(x,y)$ 。knn图在NNS中的应用最初由开创性研究[14]提出。该方法[14]首先构建数据库knn图,然后通过在该图上进行贪婪游走实现搜索。搜索过程从随机顶点开始,每一步查询从当前顶点移动到其最接近查询的邻居顶点,当查询到达局部最小值时终止。算法1展示了贪婪游走过程的伪代码。
Algorithm 1 Greedy walk
算法 1 贪婪游走
| 1: | Input: Similarity Graph Gs, similarity function s(c, y), query q, entry vertex vo |
| 2:Initialize Ucurr=Vo | |
| 3: repeat | |
| 4: | for Vadj adjacent to Ucurr in G s do |
| 5: | if s(vadj , q) < s(vcurr, q) then |
| 6: | Vcurr = Vadj |
| 7:until Ucurr changes 8:returnUcurr |
| 1: | 输入: 相似图 Gs, 相似度函数 s(c, y), 查询 q, 入口顶点 vo |
| 2: | 初始化 Ucurr=Vo |
| 3: | 重复 |
| 4: | 对于 Gs 中与 Ucurr 相邻的 Vadj 执行 |
| 5: | 如果 s(vadj, q) < s(vcurr, q) 则 |
| 6: | Vcurr = Vadj |
| 7: | 直到 Ucurr 不再变化 |
| 8: | 返回 Ucurr |
Since [14] gave rise to research on NNS with similarity graphs, a plethora of methods, which elaborate the idea, were proposed. The current state-of-the-art graph-based NNS implementations[15, 16, 17] develop additional heuristics that increase the efficiency of both graph construction and search process. Here we describe in detail the recent Navigable Small World (NSW) approach[15], as it is shown to provide the state-of-the-art for NNS[18] and its code is available online. Our approach for MIPS will be based on the NSW algorithm, although the other graph-based NNS methods[16, 17] could also be used.
自[14]开创了基于相似图(Similarity Graphs)的最近邻搜索(NNS)研究以来,涌现了大量改进该思想的算法。当前最先进的基于图的NNS实现[15,16,17]通过引入启发式策略,显著提升了图构建和搜索过程的效率。本文将详细阐述近期提出的可导航小世界(NSW)算法[15],该算法被证明在NNS领域具有最先进性能[18]且代码已开源。虽然其他基于图的NNS方法[16,17]也可行,但我们的MIPS解决方案将基于NSW算法构建。
Algorithm 2 NSW graph construction
算法 2: NSW (Navigable Small World) 图构建
The key to the practical success of NSW lies in the efficiency of both knn-graph construction and neighbor search. NSW constructs the knn-graph by adding vertices in the graph sequentially one by one. On each step NSW adds the next vertex $v$ , corresponding to a database vector $x$ to the current graph. $v$ is connected by directed edges to $M$ vertices, corresponding to the closest database vectors that are already added to the graph. The construction algorithm is presented in Algorithm 2. The primary parameter of the NSW is the maximum vertex degree $M$ , which determines the balance between the search efficiency and the probability that search stops in the suboptimal local minima. When searching via Greedy walk, NSW maintains a priority queue of a size $L$ with the knn-graph vertices, which neighbors should be visited by the search process. With $L{=}1$ the search in NSW is equivalent to Algorithm 1, while with $L>1$ it can be considered as a variant of Beam Search[19], which makes the search process less greedy. In practice, varying $L$ allows to balance between the runtime and search accuracy in NSW.
NSW实际成功的关键在于knn图构建和邻居搜索的效率。NSW通过逐个顺序添加顶点来构建knn图。每一步中,NSW将下一个顶点$v$(对应数据库向量$x$)添加到当前图中。$v$通过有向边连接到$M$个顶点,这些顶点对应已添加到图中的最近邻数据库向量。构建算法如算法2所示。NSW的主要参数是最大顶点度$M$,它决定了搜索效率与搜索陷入次优局部极小值概率之间的平衡。
当通过贪心搜索(Greedy walk)时,NSW维护一个大小为$L$的优先级队列,其中包含knn图顶点,搜索过程需要访问这些顶点的邻居。当$L{=}1$时,NSW的搜索等同于算法1;而当$L>1$时,可以将其视为集束搜索(Beam Search)[19]的一种变体,这使得搜索过程不那么贪心。实际应用中,调整$L$可以在NSW中平衡运行时间和搜索精度。
Prior work on non-metric similarity search on graphs. After the publication, we became aware of a body of previous work that explored the use of proximity graphs with general non-metric similarity functions[20, 21, 22, 23, 24]. In these works, the MIPS problem is investigated as a special case and the effectiveness of proximity graph based methods to the MIPS problem has been confirmed.
关于图上非度量相似性搜索的先前工作。在本文发表后,我们注意到已有大量前人研究探索了使用邻近图处理通用非度量相似性函数的方法 [20, 21, 22, 23, 24]。这些研究将MIPS(最大内积搜索)问题作为特例进行探讨,并证实了基于邻近图的方法对该问题的有效性。
3 Similarity graphs for MIPS
3 面向MIPS的相似度图
Now we extend the similarity graphs framework to applications with a non-metric similarity function $s(x,y)$ . Assume that we have a database $X={x_{i}\in{\mathbb{R}}^{d}|i=1,\ldots,n}$ and aim to solve the problem
现在我们将相似图框架扩展到具有非度量相似度函数$s(x,y)$的应用中。假设我们有一个数据库$X={x_{i}\in{\mathbb{R}}^{d}|i=1,\ldots,n}$,目标是解决该问题
$$
\operatorname*{argmax}_ {x_{i}\in X}s(q,x_{i}),q\in\mathbb{R}^{d}
$$
$$
\operatorname*{argmax}_ {x_{i}\in X}s(q,x_{i}),q\in\mathbb{R}^{d}
$$
3.1 Exact solution
3.1 精确解
First, let us construct a graph $G_{s}$ such that the greedy walk procedure (Algorithm 1), provides the exact answer to the problem (5). [14] has shown that for Euclidean distance $s(x,y)=-|x-y|$ , the minimal $G_{s}$ with this property is the Delaunay graph of $X$ . Now we generalize this result for a broader range of similarity functions.
首先,我们构建一个图$G_{s}$,使得贪心游走过程(算法1)能给出问题(5)的精确解。[14]已证明对于欧氏距离$s(x,y)=-|x-y|$,具有该性质的最小$G_{s}$是$X$的Delaunay图。现在我们将该结果推广到更广泛的相似度函数范围。
Definition. The $s$ -Voronoi cell $R_{k}$ , associated with the element $x_{k}\in X$ , is a set
定义。与元素 $x_{k}\in X$ 相关联的 $s$ -Voronoi 单元 $R_{k}$ 是一个集合
$$
R_{k}={x\in\mathbb{R}^{d}|s(x,x_{k})>s(x,x_{j})\forall j\neq k}
$$
$$
R_{k}={x\in\mathbb{R}^{d}|s(x,x_{k})>s(x,x_{j})\forall j\neq k}
$$
The diagrams of $s$ -Voronoi cells for $s(x,y)=-|x-y|$ and $s(x,y)=\langle x,y\rangle$ are shown on Figure 1.
图 1: 展示了 $s(x,y)=-|x-y|$ 和 $s(x,y)=\langle x,y\rangle$ 的 $s$-Voronoi 单元示意图。
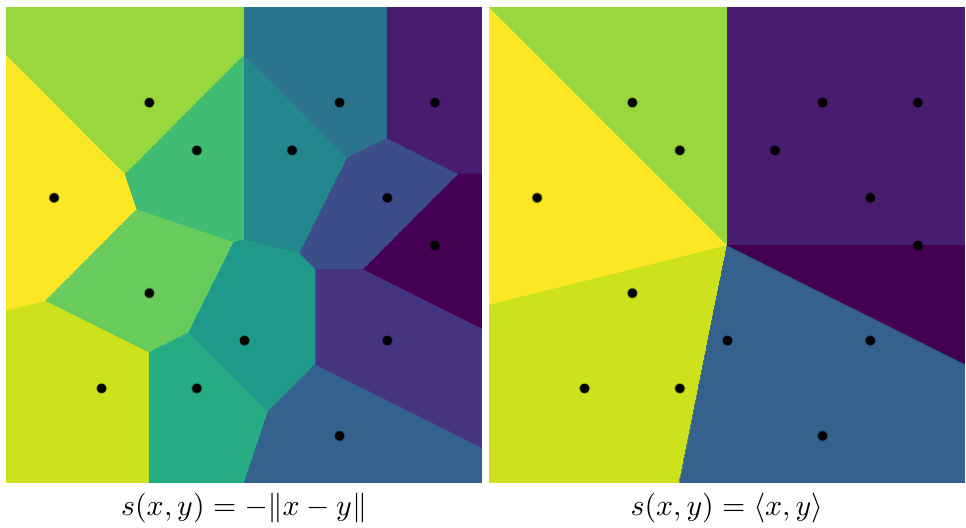
Figure 1: $s$ -Voronoi diagram examples on the plane
图 1: 平面上的 $s$ -Voronoi 图示例
Note, that in the case of inner product $s$ -Voronoi cells for some points are empty. It implies that these points can not be answers in MIPS.
注意,在内积情况下,某些点的 $s$ -Voronoi 单元为空。这意味着这些点无法作为 MIPS 的答案。
Now we can define a $s$ -Delaunay graph for a similarity function $s(x,y)$ .
现在我们能为相似度函数 $s(x,y)$ 定义一个 $s$-Delaunay图。
Definition. The $s$ -Delaunay graph for the database $X$ and the similarity function $s(x,y)$ is a graph $G_{s}(V,E)$ where the set of vertices $V$ corresponds to the set $X$ and two vertices $i$ and $j$ are connected by an edge if the corre s po ding $s$ -Voronoi cells $R_{i}$ and $R_{j}$ are adjacent in $\mathbb{R}^{d}$ .
定义。数据库 $X$ 和相似度函数 $s(x,y)$ 的 $s$-Delaunay 图是一个图 $G_{s}(V,E)$,其中顶点集 $V$ 对应于集合 $X$,且当对应的 $s$-Voronoi 单元 $R_{i}$ 和 $R_{j}$ 在 $\mathbb{R}^{d}$ 中相邻时,两个顶点 $i$ 和 $j$ 通过一条边连接。
Theorem 1. Suppose that the similarity function $s(x,y)$ is such that for every finite database $X$ the corresponding $s$ -Voronoi cells are path-connected sets. Then the greedy walk (Algorithm $I$ ) stops at the exact solution for problem (5) if the similarity graph $G_{s}$ contains the $s$ -Delaunay graph as a subgraph.
定理1. 假设相似度函数 $s(x,y)$ 满足:对于任意有限数据库 $X$,其对应的 $s$-Voronoi单元都是路径连通集。那么当相似图 $G_{s}$ 包含 $s$-Delaunay图作为子图时,贪心游走算法 (算法 $I$ ) 会在问题(5)的精确解处停止。
Proof. Assume that the greedy walk with a query $q$ stops at the point $x$ i.e. $s(x,q)>s(y,q)$ for all $y\in N(x)$ , where $N(x)$ is a set of vertices that are adjacent to $x$ . Suppose that there is a point $z\not\in N(x)$ such that $s(z,q)>s(x,q)$ . It means that the point $q$ does not belong to the $s$ -Voronoi cell $R_{x}$ corresponding to the point $x$ . Note, that if we remove all the points from $G_{s}$ except $x\cup N(x)$ , a set of points covered by $R_{x}$ does not change as all adjacent $s$ -Voronoi regions correspond to vertices from $N(x)$ and they are not removed. Hence, the query $q$ still does not belong to $R_{x}$ . Since the $s$ -Voronoi cells cover the whole space, the point $q$ belongs to some $R_{x^{\prime}},x^{\prime}\in N(x)$ . This means that $s(x^{\prime},q)>s(x,q)$ .This contradiction proves the theorem. 口
证明。假设针对查询$q$的贪婪游走停止于点$x$,即对于所有$y\in N(x)$,有$s(x,q)>s(y,q)$,其中$N(x)$表示与$x$相邻的顶点集合。若存在点$z\not\in N(x)$满足$s(z,q)>s(x,q)$,则说明查询点$q$不属于$x$对应的$s$-Voronoi单元$R_{x}$。值得注意的是,若从图$G_{s}$中移除除$x\cup N(x)$外的所有顶点,$R_{x}$所覆盖的点集不会改变——因为所有相邻的$s$-Voronoi区域都对应于$N(x)$中的顶点且未被移除。因此,查询$q$仍不属于$R_{x}$。由于$s$-Voronoi单元覆盖整个空间,点$q$必属于某个$x^{\prime}\in N(x)$对应的$R_{x^{\prime}}$,这意味着$s(x^{\prime},q)>s(x,q)$。该矛盾证明了定理成立。口
Now we show that $s(x,y)=\langle x,y\rangle$ satisfies the assumptions of the Theorem.
现在我们证明 $s(x,y)=\langle x,y\rangle$ 满足该定理的假设条件。
Lemma 1. Suppose $X$ is a finite database and the similarity function $s(x,y)$ is linear, then the $s$ -Voronoi cells are convex.
引理 1. 假设 $X$ 是一个有限数据库且相似度函数 $s(x,y)$ 是线性的,那么 $s$-Voronoi 单元是凸的。
Proof. Consider a $s$ -Voronoi cell $R_{x}$ , corresponding to a point $x\in X$ . Let us take two arbitrary vectors $u$ and $v$ from the $s$ -Voronoi cell $R_{x}$ . It means that
证明。考虑一个 $s$-Voronoi 单元 $R_{x}$,对应于点 $x\in X$。取 $s$-Voronoi 单元 $R_{x}$ 中的任意两个向量 $u$ 和 $v$。这意味着
$$
\begin{array}{r}{s(x,u)>s(w,u)\forall w\in X\setminus{x}}\ {s(x,v)>s(w,v)\forall w\in X\setminus{x}}\end{array}
$$
$$
\begin{array}{r}{s(x,u)>s(w,u)\forall w\in X\setminus{x}}\ {s(x,v)>s(w,v)\forall w\in X\setminus{x}}\end{array}
$$
Hence, due to linearity
因此,由于线性
$$
s(x,t u+(1-t)v)>s(w,t u+(1-t)v),t\in[0,1]
$$
$$
s(x,t u+(1-t)v)>s(w,t u+(1-t)v),t\in[0,1]
$$
Therefore, vector $t u+(1-t)v\in R_{x}$ for every $t\in[0,1]$ .
因此,向量 $t u+(1-t)v\in R_{x}$ 对于每个 $t\in[0,1]$ 都成立。
Corollary 1. If the graph $G(V,E)$ contains the $s$ -Delaunay graph for the similarity function $s(x,y)=\langle x,y\rangle$ then greedy walk always gives the exact true answer for MIPS.
推论1. 若图 $G(V,E)$ 包含相似度函数 $s(x,y)=\langle x,y\rangle$ 的 $s$-Delaunay图,则贪心游走总能给出MIPS问题的精确解。
Proof. Due to Lemma 1 all $s$ -Voronoi cells for $s(x,y)=\langle x,y\rangle$ are convex, therefore, path-connected. 口
证明。根据引理1,对于 $s(x,y)=\langle x,y\rangle$ 的所有 $s$-Voronoi单元都是凸的,因此是路径连通的。口
3.2 $s$ -Delaunay graph approximation for MIPS
3.2 用于MIPS的$s$-Delaunay图近似
In practice, the computation and usage of the exact $s$ -Delaunay graph in high-dimensional spaces are infeasible due to the exponentially growing number of edges[25]. Instead, we approximate the $s$ -Delaunay graph as was previously proposed for Euclidean distance case in [16, 17, 15]. In particular, we adopt the approximation proposed in [15] by simply extending Algorithm 2 to inner product similarity function $\bar{s}(x,y)=\langle{x},\bar{y}\rangle$ . As in [15] we also restrict the vertex degree to a constant $M$ , which determines the $s$ -Delaunay graph approximation quality. We refer to the proposed MIPS method as ip-NSW. The search process in ip-NSW remains the same as in [15] except that the inner product similarity function guides the similarity graph exploration.
实践中,由于边数呈指数级增长[25],在高维空间中计算和使用精确的 $s$-Delaunay图是不可行的。我们转
