AD-AutoGPT: An Autonomous GPT for Alzheimer’s Disease Info demi ology
AD-AutoGPT: 用于阿尔茨海默病信息学的自主GPT
Haixing $\mathbf{Dai}^{\mathbf{1}}$ , Yiwei $\mathbf{Li^{1}}$ , Zhengliang $\mathbf{Liu^{1}}$ , Lin Zhao1, Zihao $\mathbf{W}\mathbf{u}^{\mathbf{1}}$ , Suhang $\mathbf{Song^{2}}$ , Ye $\mathbf{Shen^{3}}$ , Dajiang $\mathbf{Zhu^{4}}$ , Xiang $\mathbf{Li^{5,6}}$ , Sheng $\mathbf{Li^{7}}$ , Xiaobai $\mathbf{Yao^{8}}$ , Lu $\mathbf{Shi^{9}}$ , Quanzheng $\mathbf{Li^{5,6}}$ , Zhuo Chen2, Donglan Zhang10, Gengchen $\mathbf{Mai^{8,1^{* }}}$ , Tianming Liu1* *
Haixing $\mathbf{Dai}^{\mathbf{1}}$,Yiwei $\mathbf{Li^{1}}$,Zhengliang $\mathbf{Liu^{1}}$,Lin Zhao1,Zihao $\mathbf{W}\mathbf{u}^{\mathbf{1}}$,Suhang $\mathbf{Song^{2}}$,Ye $\mathbf{Shen^{3}}$,Dajiang $\mathbf{Zhu^{4}}$,Xiang $\mathbf{Li^{5,6}}$,Sheng $\mathbf{Li^{7}}$,Xiaobai $\mathbf{Yao^{8}}$,Lu $\mathbf{Shi^{9}}$,Quanzheng $\mathbf{Li^{5,6}}$,Zhuo Chen2,Donglan Zhang10,Gengchen $\mathbf{Mai^{8,1^{* }}}$,Tianming Liu1* *
Received: date / Accepted: date
收稿日期:date / 录用日期:date
Haixing Dai E-mail: hd54134@uga.edu
Haixing Dai 电子邮箱:hd54134@uga.edu
Yiwei Li E-mail: yl80817@uga.edu
Yiwei Li 电子邮箱: yl80817@uga.edu
Zhengliang Liu E-mail: zl18864@uga.edu
Zhengliang Liu E-mail: zl18864@uga.edu
Lin Zhao E-mail: lin.zhao@uga.edu
Lin Zhao 电子邮箱: lin.zhao@uga.edu
Zihao Wu E-mail: zw63397@uga.edu
吴子豪 电子邮箱:zw63397@uga.edu
Suhang Song E-mail: suhang.song@uga.edu
Suhang Song 电子邮箱: suhang.song@uga.edu
Ye Shen E-mail: yeshen@uga.edu
叶申 电子邮箱: yeshen@uga.edu
Dajiang Zhu E-mail: dajiang.zhu@uta.edu
Dajiang Zhu E-mail: dajiang.zhu@uta.edu
Xiang Li E-mail: xli60@mgh.harvard.edu
项立 E-mail: xli60@mgh.harvard.edu
Sheng Li E-mail: li sheng 1989@gmail.com
Sheng Li 邮箱:li sheng 1989@gmail.com
Xiaobai Yao E-mail: xyao@uga.edu
Xiaobai Yao 电子邮箱: xyao@uga.edu
Lu Shi E-mail: LUS@clemson.edu
Lu Shi E-mail: LUS@clemson.edu
Quanzheng Li
Quanzheng Li
Abstract In this pioneering study, inspired by AutoGPT, the state-of-the-art open-source application based on the GPT-4 large language model, we develop a novel tool called AD-AutoGPT which can conduct data collection, processing, and analysis about complex health narratives of Alzheimer’s Disease in an autonomous manner via users’ textual prompts. We collated comprehensive data from a variety of news sources, including the Alzheimer’s Association, BBC, Mayo Clinic, and the National Institute on Aging since June 2022, leading to the autonomous execution of robust trend analyses, intertopic distance maps visualization, and identification of salient terms pertinent to Alzheimer’s Disease. This approach has yielded not only a quantifiable metric of relevant discourse but also valuable insights into public focus on Alzheimer’s Disease. This application of AD-AutoGPT in public health signifies the transformative potential of AI in facilitating a data-rich understanding of complex health narratives like Alzheimer’s Disease in an autonomous manner, setting the groundwork for future AI-driven investigations in global health landscapes.
摘要 在这项开创性研究中,我们受基于GPT-4大语言模型的最先进开源应用AutoGPT启发,开发了名为AD-AutoGPT的新型工具。该工具能通过用户文本提示,自主完成阿尔茨海默病复杂健康叙事的采集、处理与分析工作。我们整合了自2022年6月以来阿尔茨海默病协会、BBC、梅奥诊所及美国国家老龄化研究所等多渠道的全面数据,实现了趋势分析、主题间距可视化及疾病相关核心术语识别的自主化执行。该方法不仅产出了可量化的相关论述指标,更揭示了公众对阿尔茨海默病的关注焦点。AD-AutoGPT在公共卫生领域的应用,彰显了AI以自主方式促进对阿尔茨海默病等复杂健康叙事进行数据化理解的变革潜力,为未来全球卫生领域AI驱动研究奠定了基础。
Keywords AutoGPT · GPT-4 · Alzheimer’s Disease · Info demi ology
关键词 AutoGPT · GPT-4 · 阿尔茨海默病 · 信息流行病学
Mathematics Subject Classification (2020) MSC code1 · MSC code2 more
数学学科分类(2020)MSC code1 · MSC code2 更多
� Tianming Liu E-mail: tliu@uga.edu
Tianming Liu E-mail: tliu@uga.edu
1 Introduction
1 引言
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD), a progressive neuro degenerative disorder, remains one of the most pressing public health concerns globally in the 21st century [1,2]. This disease, characterized by cognitive impairments such as memory loss, predominantly affects aging populations, exerting an escalating burden on global healthcare systems as societies continue to age [3]. The significance of AD is further magnified by the increasing life expectancy globally, with the disease now recognized as a leading cause of disability and dependency among older people [4]. Consequently, AD has substantial social, economic, and health system implications, making its understanding and awareness of paramount importance [5,6].
阿尔茨海默病 (AD) 是一种进行性神经退行性疾病,仍是21世纪全球最紧迫的公共卫生问题之一 [1,2]。该疾病以记忆力减退等认知障碍为特征,主要影响老年人群,随着社会持续老龄化,其对全球医疗系统的负担日益加重 [3]。全球预期寿命的延长进一步凸显了AD的重要性,该病现已被认定为老年人致残和丧失生活自理能力的主要原因 [4]。因此,AD对社会、经济和卫生系统具有重大影响,这使得对其认知与了解变得至关重要 [5,6]。
Despite the ubiquity and severity of AD, a gap persists in comprehensive, data-driven public understanding of this complex health narrative. Traditionally, public health professionals have to rely on labor-intensive methods such as web scraping, API data collection, data post processing, and analysis/synthesis to gather insights from news media, health reports, and other textual sources [7,8,9]. However, these methods often necessitate complex pipelines for data gathering, processing, and analysis. Moreover, the sheer scale of global data presents an ever-increasing challenge, one that demands a novel, innovative approach to streamline these processes and extract valuable, actionable insights efficiently and automatically. In addition, the technical expertise required for developing data processing and analysis pipelines significantly limits the access and engagement of the broader public health community.
尽管阿尔茨海默病(AD)普遍存在且危害严重,但公众对这种复杂健康议题的全面数据驱动认知仍存在空白。传统上,公共卫生专业人员必须依赖网络爬取、API数据采集、数据后处理及分析综合等劳动密集型方法[7,8,9],从新闻媒体、健康报告等文本来源获取洞见。然而这些方法通常需要构建复杂的数据采集-处理-分析流水线,且全球数据规模带来的挑战与日俱增,亟需创新方法来实现流程自动化、高效提取可操作的见解。此外,开发数据处理分析流水线所需的技术专长,极大限制了更广泛公共卫生群体的参与度。
AutoGPT [10] is an experimental open-source application that harnesses the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-4 [11] and ChatGPT [12] to automate and optimize the analytical process. With its advanced linguistic understanding and autonomous operation, AutoGPT simplifies complex data pipelines, facilitating comprehensive analyses of vast datasets with simple textual prompts. This tool transcends traditional limitations, unlocking the potential of LLMs for autonomous data collection, processing, summarization, analysis, and synthesis. In this study, we modify the AutoGPT architecture into public health applications and develop AD-AutoGPT to analyze a multitude of news sources, including the Alzheimer’s Association, BBC, Mayo Clinic, and the National Institute on Aging, focusing on discourse since June 2022. We are among the pioneers in integrating AutoGPT into public health informatics, adapting this transformative AI tool into the public health domain to elucidate the complex narrative surrounding Alzheimer’s Disease. This research underlines the enormous potential of autonomous LLMs in global health research, paving the way for future AI-assisted investigations into various health-related domains.
AutoGPT [10] 是一款实验性开源应用程序,它利用 GPT-4 [11] 和 ChatGPT [12] 等大语言模型 (LLM) 的能力来自动化和优化分析流程。凭借其先进的语言理解能力和自主操作特性,AutoGPT 简化了复杂的数据管道,仅需简单的文本提示即可实现对海量数据集的全面分析。该工具突破了传统限制,释放了大语言模型在自主数据收集、处理、汇总、分析和综合方面的潜力。在本研究中,我们将 AutoGPT 架构改造为公共卫生应用,并开发了 AD-AutoGPT 来分析包括阿尔茨海默病协会、BBC、梅奥诊所和美国国家老龄化研究所在内的多种新闻来源,重点关注自 2022 年 6 月以来的相关论述。我们是首批将 AutoGPT 整合到公共卫生信息学中的研究者之一,将这一变革性 AI 工具应用于公共卫生领域,以阐明围绕阿尔茨海默病的复杂叙事。这项研究凸显了自主大语言模型在全球健康研究中的巨大潜力,为未来 AI 辅助各类健康相关领域研究铺平了道路。
We summarize our key contributions below:
我们在下方总结了关键贡献:
– Inspired by AutoGPT, we develop a novel LLM-based tool called ADAutoGPT, which can generate data collection, processing, and analysis pipeline in an autonomous manner based on users’ textual prompts. More specifically, we adapt AD-AutoGPT to the public health domain to showcase its great potential of autonomous pipeline generation to understand the complex narrative surrounding Alzheimer’s Disease.
受AutoGPT启发,我们开发了一款基于大语言模型(LLM)的创新工具ADAutoGPT,能够根据用户文本提示(prompt)自主生成数据收集、处理及分析流程。具体而言,我们将ADAutoGPT适配至公共卫生领域,通过构建阿尔茨海默症(Alzheimer's Disease)相关复杂叙事的理解流程,展示其自主生成分析管道的强大潜力。
– While AutoGPT is an effective autonomous LLM-based tool, it has lots of limitations when applying it on AD Info demi ology during the process of public health information retrieval, text-based information extraction, text sum mari z ation, summary analysis, and visualization. To overcome AutoGPT’s limitations for the AD Info demi ology task, AD-AutoGPT provides the following improvements: 1) specific prompting mechanisms to improve the efficiency and accuracy of AD information retrieval; 2) a tailored spatio temporal information extraction functionality; 3) an improved text sum- marization ability; 4) an in-depth analysis ability on generated text summaries; and 5) an effective and dynamic visualization capability.
虽然AutoGPT是一种有效的基于大语言模型的自主工具,但在应用于AD信息流行病学领域的公共卫生信息检索、文本信息提取、文本摘要、摘要分析和可视化过程中仍存在诸多局限。为克服AutoGPT在AD信息流行病学任务中的不足,AD-AutoGPT提供了以下改进:1) 采用特定提示机制提升AD信息检索效率与准确性;2) 定制化时空信息提取功能;3) 增强的文本摘要能力;4) 对生成文本摘要的深度分析能力;5) 高效动态的可视化功能。
– We show that AD-AutoGPT transforms the traditional labor-intensive data collection, processing, and analysis paradigm into a prompt-based automated, and optimized analytical framework. This has allowed for efficient, comprehensive analysis of numerous news sources related to Alzheimer’s Disease.
- 我们展示了AD-AutoGPT如何将传统劳动密集型的数据收集、处理和分析范式转变为基于提示词(prompt)的自动化优化分析框架。这使得对大量阿尔茨海默病相关新闻源的高效全面分析成为可能。
– Through AD-AutoGPT, we have provided a case study for detailed trend analysis, intertopic distance mapping, and identified salient terms related to Alzheimer’s Disease from four AD-related new sources. This contributes significantly to the existing body of knowledge and facilitates a nuanced understanding of the disease’s discourse in public health.
- 通过AD-AutoGPT,我们提供了一个案例研究,用于详细分析阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer’s Disease)的趋势、绘制主题间距离图,并从四个AD相关新闻来源中识别出关键术语。这显著丰富了现有知识体系,并促进了对公共卫生领域疾病讨论的细致理解。
– Our research underlines the capacity of AD-AutoGPT to facilitate datadriven public understanding of complex health narratives, such as Alzheimer’s Disease, which is of paramount importance in an aging global society.
我们的研究强调了AD-AutoGPT在促进数据驱动的公众理解复杂健康叙事(如阿尔茨海默病)方面的能力,这在全球老龄化社会中至关重要。
– The methodologies and insights from our work provide a foundation for future AI-assisted public health research. Our AD-AutoGPT pipeline is extendable to other topics in public health or even other domains. This work paves the way for comprehensive and efficient investigations into various domains.
- 我们的工作方法和见解为未来AI辅助的公共卫生研究奠定了基础。AD-AutoGPT流程可扩展至公共卫生其他主题甚至其他领域,为全面高效探索多领域研究铺平了道路。
2 Related Work
2 相关工作
2.1 Large Language Models
2.1 大语言模型 (Large Language Models)
Large language models (LLMs), with their origins in Transformer-based pretrained language models (PLMs) such as BERT [13] and GPT [14], have substantially transformed the field of natural language processing (NLP). LLMs have superseded previous methods such as Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) based models, leading to their widespread adoption across various NLP tasks [12,15]. Furthermore, the emergence of very large language models such as GPT-3 [16], Bloom [17], GPT-4 [11], PaLM [18], and PaLM-2 [19] demonstrates a clear trend towards even more sophisticated language understanding capabilities.
大语言模型 (LLMs) 起源于基于Transformer的预训练语言模型 (PLMs) ,例如BERT [13]和GPT [14] ,它们彻底改变了自然语言处理 (NLP) 领域。大语言模型取代了基于循环神经网络 (RNN) 等传统方法,在各种NLP任务中得到广泛应用 [12,15] 。此外,GPT-3 [16] 、Bloom [17] 、GPT-4 [11] 、PaLM [18] 和PaLM-2 [19] 等超大规模语言模型的出现,展现了语言理解能力向更复杂方向发展的明显趋势。
These models are designed to learn accurate contextual latent feature represent at ions from input text [20], which can then be employed in a variety of applications, including question answering, information extraction, sentiment analysis, text classification, and text generation. The innovative technique of reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) [21] has been used to further align LLMs with human preferences, which has found applications in Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) models such as Instruct GP T [22], Sparrow [23], and ChatGPT [12]. More recently, GPT-4 has significantly advanced the state-of-the-art of language models, opening up new opportunities for LLM applications.
这些模型旨在从输入文本中学习精确的上下文潜在特征表示 [20],可应用于问答、信息抽取、情感分析、文本分类和文本生成等多种场景。基于人类反馈的强化学习 (RLHF) [21] 这一创新技术被用于进一步使大语言模型与人类偏好对齐,该技术已在通用人工智能 (AGI) 模型中得到应用,例如 Instruct GPT [22]、Sparrow [23] 和 ChatGPT [12]。最近,GPT-4 显著推进了语言模型的技术前沿,为大语言模型应用开辟了新机遇。
Other than the applications in NLP domain, LLMs also show promising results and significant impacts in other disciplines such as biology [24], geography [25,26], agriculture [27], education [28,29], medical and health care [30, 31], and so on.
除了在自然语言处理(NLP)领域的应用外,大语言模型(LLM)在生物学[24]、地理学[25,26]、农业[27]、教育学[28,29]、医疗健康[30,31]等其他学科中也展现出显著成效和深远影响。
2.2 Public Health Info demi ology
2.2 公共卫生信息流行病学
Info demi ology [32] is a field that studies the determinants and distribution of information on the internet or in a population, with the goal of informing public health and public policy [32,9]. The term combines "information" and "epidemiology" and is a recognized approach in public health informatics, providing insights into health-related behaviors and perceptions. It plays a crucial role in monitoring and managing the information epidemic ("infodemic") associated with major public health crises.
信息流行病学 [32] 是研究互联网或人群中信息的决定因素与分布规律的学科,旨在为公共卫生和公共政策提供依据 [32,9]。该术语由"信息"和"流行病学"组合而成,是公共卫生信息学领域的公认方法,可揭示健康相关行为与认知。它在监测和管理重大公共卫生危机伴随的信息疫情 ("infodemic") 方面发挥着关键作用。
For example, Piamonte et al. [33] analyzed global search queries for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) using Google Trends data, comparing this online interest (Search Volume Index) with measures of disease burden. The study revealed that search behavior and interest in AD were influenced by factors like news about celebrities with AD and awareness months, and also highlighted potential correlations between this online interest and socioeconomic development.
例如,Piamonte等人[33]利用Google Trends数据分析了全球关于阿尔茨海默病(AD)的搜索查询,将这种在线关注度(搜索量指数)与疾病负担指标进行了比较。该研究表明,AD相关搜索行为和关注度受到名人患AD新闻和疾病宣传月等因素的影响,并揭示了这种在线关注度与社会经济发展之间可能存在的关联性。
With the rise of the internet and digital technologies, info demi ology provides a vital lens to examine the flow of health information and misinformation, helping public health practitioners develop effective communication strategies and interventions [34,35]. In the context of Alzheimer’s disease, understanding online behaviors and interests via info demi ology can help enhance public awareness, correct misconceptions, and inform preventative and management strategies for the disease [33,36].
随着互联网和数字技术的兴起,信息流行病学 (infodemiology) 为审视健康信息和错误信息的传播提供了重要视角,帮助公共卫生从业者制定有效的传播策略和干预措施 [34,35]。在阿尔茨海默病的背景下,通过信息流行病学理解在线行为和兴趣有助于提升公众认知、纠正误解,并为该疾病的预防和管理策略提供依据 [33,36]。
2.3 AutoGPT and LLM Automation
2.3 AutoGPT 与大语言模型自动化
The development and use of AutoGPT, LangChain $^{1}$ , and many other automation techniques for LLMs represent a significant advancement in the field of
AutoGPT、LangChain$^{1}$等大语言模型(LLM)自动化技术的开发与应用,标志着该领域的重大进展
NLP and artificial intelligence. AutoGPT builds on the successes of large language models like GPT-3 and GPT-4, but takes automation a step further by providing a more user-friendly interface for non-expert users [10].
自然语言处理与人工智能。AutoGPT基于GPT-3和GPT-4等大语言模型的成功,通过为非专业用户提供更友好的界面 [10],将自动化推向新高度。
With AutoGPT, complex tasks such as data collection, data cleaning, analysis, and even the generation of human-like text can be completed using straightforward prompts, removing the need for extensive coding or data science expertise. This has the potential to democratize access to powerful language model technology, opening up new possibilities for research and application in a wide range of fields, including public health.
借助AutoGPT,数据收集、数据清洗、分析乃至生成类人文本等复杂任务,仅需简单提示即可完成,无需大量编码或数据科学专业知识。这一技术有望降低大语言模型的使用门槛,为公共卫生等广泛领域的研究与应用开辟新可能。
Recent studies [37,38] have highlighted the potential of AutoGPT and similar tools for automating the retrieval and analysis of large datasets. For example, with a well-formulated query, AutoGPT can be directed to crawl through a wide array of online platforms, collecting and analyzing comments, discussions, and posts pertaining to vaccines. The system would subsequently generate a summarizing report, outlining major themes of public opinion and prevalent misconceptions, thereby providing valuable insights for public health officials in formulating targeted communication and intervention strategies.
近期研究[37,38]指出AutoGPT等工具在自动化检索与分析大规模数据集方面的潜力。例如,通过精心设计的查询指令,可引导AutoGPT爬取各类网络平台,收集并分析与疫苗相关的评论、讨论及帖子。该系统随后会生成总结报告,概述舆论主要观点及常见误解,从而为公共卫生官员制定精准传播与干预策略提供关键洞见。
In the context of info demi ology, AutoGPT can automate the process of analyzing online health information trends, which traditionally involves extensive manual effort. Specifically, it can efficiently scan and interpret internet data, track the spread of health information and misinformation, assess public reaction to health policies or events, and potentially predict future trends.
在信息流行病学 (infodemiology) 背景下,AutoGPT 可自动化分析在线健康信息趋势这一传统上需要大量人工干预的过程。具体而言,它能高效扫描和解析互联网数据、追踪健康信息与错误信息的传播路径、评估公众对卫生政策或事件的反应,并具备预测未来趋势的潜力。
2.4 Improving Autonomous LLM-based Tools for Public Health
2.4 提升基于大语言模型的公共卫生自主工具
While recognizing the potential of autonomous large language models (LLMs) like AutoGPT in public health research and practice, we identified certain limitations in their current state that may hinder their efficacy in particular use cases, such as info demi ology. By tailoring these tools to the specific needs of public health professionals, we aim to enhance their utility in these contexts.
在认识到诸如AutoGPT等自主大语言模型(LLM)在公共卫生研究和实践中的潜力的同时,我们也发现了它们在当前状态下存在的一些局限性,这些局限性可能会阻碍其在特定用例(如信息流行病学)中的有效性。通过针对公共卫生专业人员的具体需求定制这些工具,我们旨在提升它们在这些场景中的实用性。
Firstly, despite AutoGPT’s extensive searching capabilities, its ability to acquire specialized information quickly and precisely, for instance, about Alzheimer’s disease (AD), can be somewhat limited. In response to this, we have integrated specific prompting mechanisms in our model, AD-AutoGPT. These tailored prompts direct AD-AutoGPT to gather data from a select list of authoritative websites relevant to AD, which enhances the efficiency and relevance of information acquisition.
首先,尽管AutoGPT具备广泛的搜索能力,但其快速精准获取专业信息(例如阿尔茨海默病(AD)相关)的能力仍存在一定局限。为此,我们在AD-AutoGPT模型中整合了特定提示机制。这些定制化提示会引导AD-AutoGPT从精选的AD权威网站列表中采集数据,从而提升信息获取的效率和相关性。
Secondly, Our AD-AutoGPT model also addresses the challenge AutoGPT faces in extracting critical details such as the time and place of news events from articles accurately. AD-AutoGPT uses web-crawling scripts to extract accurate timestamps from news pieces, and employs geo-location libraries such as geopy [39] and geopandas [40] to retrieve precise location information from texts.
其次,我们的AD-AutoGPT模型还解决了AutoGPT在从文章中准确提取新闻事件时间和地点等关键细节时面临的挑战。AD-AutoGPT使用网络爬虫脚本从新闻中提取准确的时间戳,并利用geopy [39]和geopandas [40]等地理定位库从文本中检索精确的位置信息。
Thirdly, depth of analysis is another area where AutoGPT could benefit from further refinement. Owing to the token limit in models like ChatGPT,
第三,分析深度是AutoGPT可以进一步改进的另一个领域。由于ChatGPT等模型中的Token限制,
AutoGPT’s analysis is often restricted to the first 4096 tokens [12]. Consequently, it might miss core content or important details. To overcome this limitation, AD-AutoGPT segments the text, vectorizes it, and then processes these chunks independently. It creates summaries for each of these segments and then amalgamates these summaries to create a comprehensive representation of the news article.
AutoGPT的分析通常局限于前4096个token [12],因此可能遗漏核心内容或重要细节。为突破这一限制,AD-AutoGPT采用文本分块、向量化处理后独立处理各片段的方式。它会为每个文本块生成摘要,再将这些摘要整合形成新闻文章的完整表征。
Fourthly, AutoGPT’s current capabilities, while useful, lack the capacity to conduct an in-depth analysis of the generated summaries. The synthesized data can still be redundant and may not accurately capture the most essential information. In contrast, AD-AutoGPT applies Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) [41] to extract the most pertinent keywords from the text summaries, offering users a succinct understanding of the central themes in the Alzheimer’s disease domain.
第四,AutoGPT目前的功能虽然实用,但缺乏对生成摘要进行深入分析的能力。合成的数据可能仍然冗余,且未必能准确捕捉最关键的信息。相比之下,AD-AutoGPT采用潜在狄利克雷分配 (LDA) [41] 从文本摘要中提取最相关的关键词,为用户提供对阿尔茨海默病领域核心主题的简明理解。
Lastly, while AutoGPT is effective at generating text-based information, it lacks robust visualization capabilities. Addressing this limitation, AD-AutoGPT integrates dynamic visualization techniques, creating plots of news occurrences over time, highlighting locations where news events are happening, and even illustrating the evolution of research keywords over time.
最后,虽然AutoGPT在生成基于文本的信息方面很有效,但它缺乏强大的可视化能力。针对这一局限,AD-AutoGPT集成了动态可视化技术,可绘制新闻事件随时间变化的图表、突出显示新闻事件发生的地点,甚至展示研究关键词随时间的演变趋势。
AD-AutoGPT is refined through the application of domain-specific knowledge and technical adjustments to optimize its relevance and effectiveness for public health researchers and practitioners. As a result, AD-AutoGPT is faster and more efficient in its operations compared to the original AutoGPT, highlighting the advantages of tailoring autonomous LLM-based tools for specific use cases in public health.
AD-AutoGPT通过应用领域特定知识和技术调整进行优化,以提升其在公共卫生研究人员和实践者中的相关性和有效性。因此,与原始AutoGPT相比,AD-AutoGPT运行速度更快、效率更高,突显了针对公共卫生特定用例定制基于大语言模型的自主工具的优势。
3 Method
3 方法
In this section, we will introduce AD-AutoGPT, an LLM-based tool we developed to automate the process of Alzheimer’s Disease Info demi ology. ADAutoGPT uses the Langchain framework to realize the connection with GPT-4 and ChatGPT API, and establish an LLM-based autonomous framework with a chain of thinking mode for Alzheimer’s disease. This is a model that can automatically search for the latest news, extract meaningful spatio-temporal data, summarize the news, analysis news content, and visualize analysis results. The overall framework of AD-AutoGPT is shown in Figure 1. We construct an instruction library that contains a set of possible commands/tools we have developed to achieve the public health info demi ology task. A prompt shown in Figure 2a is designed to facilitate LLMs to identify usable tools from the instruction library and form a data processing pipeline that demonstrates the process of thinking. AD-AutoGPT’s ability of “translating” natural language prompts to real data processing pipeline is similar to the idea of semantic parsing used in traditional question answering literature [42,43,44], which aims at translating a natural language question into an executable query for a given database or knowledge base. However, the difference is that semantic parsing is only able to generate rather simple executable queries on a well-defined knowledge base while our AD-AutoGPT can handle much more complex realworld tasks such as searching and collecting news from Google, analyzing new contents, and visualizing topic trends and spatial-temporal distributions of news. Below we will introduce the workflow of AD-AutoGPT and the basic principles of the algorithms used in the workflow in detail.
在本节中,我们将介绍AD-AutoGPT,这是我们开发的一款基于大语言模型的工具,用于自动化阿尔茨海默病信息流行病学处理流程。AD-AutoGPT利用Langchain框架实现与GPT-4和ChatGPT API的对接,构建了一个基于大语言模型、采用思维链模式的阿尔茨海默病自主分析框架。该模型能够自动搜索最新资讯、提取有价值的时空数据、生成新闻摘要、分析内容并可视化分析结果。AD-AutoGPT的整体框架如图1所示。
我们构建了一个指令库,其中包含为完成公共卫生信息流行病学任务而开发的一系列命令/工具。如图2a所示的提示词设计用于帮助大语言模型从指令库中识别可用工具,并形成展现思维过程的数据处理流程。AD-AutoGPT将自然语言提示"翻译"为实际数据处理流程的能力,与传统问答文献[42,43,44]中使用的语义解析思想类似,后者旨在将自然语言问题转化为针对特定数据库或知识库的可执行查询。不同之处在于,语义解析只能在结构明确的知识库上生成相对简单的可执行查询,而我们的AD-AutoGPT能处理更复杂的现实任务,例如从Google搜索采集新闻、分析内容、可视化主题趋势和新闻时空分布等。下文将详细说明AD-AutoGPT的工作流程及所用算法的基本原理。
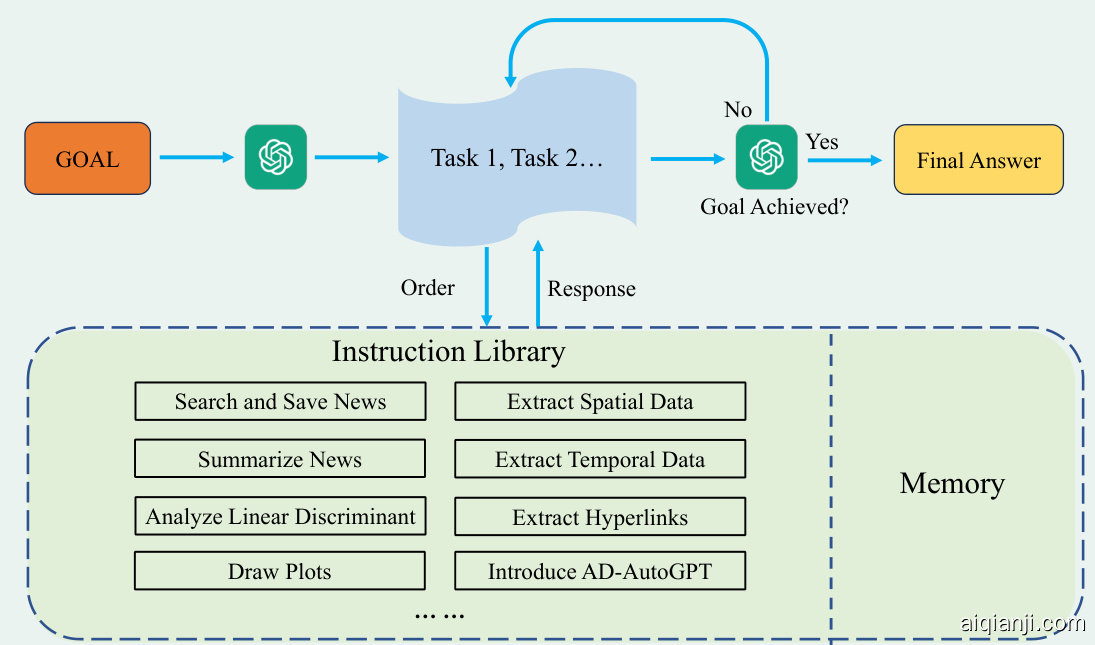
Fig. 1: The basic framework of AD-AutoGPT. The instruction library contains a set of possible commands we have developed to complete the public health info demi ology task. These commands can also be expanded in the future. In order to achieve the goal, AD-AutoGPT will access GPT-4 and divide the final goal into several smaller tasks, and then solve small tasks step-by-step by choosing the most appropriate command for the sub-task in the instruction library. After thinking and judging, if the final goal has not been achieved, AD-AutoGPT will continue to split the task and execute the command. If the final goal has been achieved, AD-AutoGPT will return the final answer.
图 1: AD-AutoGPT的基本框架。指令库包含一组我们开发的用于完成公共卫生信息流行病学任务的命令,这些命令未来还可扩展。为实现目标,AD-AutoGPT会访问GPT-4并将最终目标拆分为若干子任务,随后通过从指令库中选择最适合子任务的命令逐步解决这些小任务。经过思考判断后,若最终目标未达成,AD-AutoGPT会继续拆分任务并执行命令;若目标已达成,则返回最终答案。
3.1 Overall Framework
3.1 整体框架
Our primary goal is to learn from the chain thinking mode of AutoGPT to realize the automatic collection and summary of Alzheimer’s disease news. To achieve this goal, the power of LLMs must be used. Advanced LLMs such as ChatGPT and GPT-4 have brought earth-shaking changes to the NLP domain, and we see the potential advantages of LLMs for the public health field.
我们的主要目标是借鉴AutoGPT的链式思考模式,实现阿尔茨海默病新闻的自动采集与汇总。为实现这一目标,必须借助大语言模型的力量。ChatGPT、GPT-4等先进大语言模型已为自然语言处理领域带来颠覆性变革,我们看到了这类模型在公共卫生领域的潜在优势。
The overall framework is shown in Figure 1. For the target task, ADAutoGPT will use ChatGPT or GPT-4 to divide the target task into several small tasks and process them separately. We provide AD-AutoGPT with an instruction library which contains customized functions/tools including:
整体框架如图 1 所示。针对目标任务,ADAutoGPT 会使用 ChatGPT 或 GPT-4 将目标任务拆分为若干小任务并分别处理。我们为 AD-AutoGPT 提供了包含以下定制化功能/工具的指令库:
After operating every small task choosing from these tools, AD-AutoGPT will judge whether the overall goal has been achieved according to the running results of the function, or it needs to think again and solve the next small problem. Chain thinking is realized through such a pattern. If during the process AD-AutoGPT thinks that the system has reached the initial goal, the system will exit and return a final answer to the initial question.
在从这些工具中选择并执行每个小任务后,AD-AutoGPT会根据函数的运行结果判断整体目标是否达成,或者是否需要重新思考并解决下一个小问题。通过这种模式实现了链式思考。如果AD-AutoGPT认为系统已达到初始目标,系统将退出并向初始问题返回最终答案。
3.2 Designing Prompts to Implement Chain of Thoughts
3.2 设计提示以实现思维链
A prompt example can be seen in Figure 2a and the model thinking process of AD-AutoGPT is shown in Figure 2b. According to the input, this prompt has four parts in the task process which are question, thought, action, and action input.
提示示例如图 2a 所示,AD-AutoGPT 的模型思考过程如图 2b 所示。根据输入内容,该提示在任务过程中包含四个部分:问题 (question)、思考 (thought)、行动 (action) 和行动输入 (action input)。
For output, a prompt has three parts which are observation, thought, and final answer.
输出时,提示包含三个部分:观察、思考和最终答案。
The last part of the prompt is the question entered by the user, such as the question in Figure 2a, "Can you help me to know something new about Alzheimer’s Disease and maybe draw some plots for me? ". AI will decompose the complex target tasks proposed by users into several simple tasks, thus inspiring a chain of thoughts. And the thinking process of AI can be seen in Figure 2b
提示的最后部分是用户输入的问题,例如图 2a 中的问题 "你能帮我了解一些关于阿尔茨海默病的新知识,并为我绘制一些图表吗?"。AI 会将用户提出的复杂目标任务分解为几个简单任务,从而激发思维链。AI 的思考过程可以在图 2b 中看到。
Owing to this set of prompts, we can ensure that the thinking logic of ADAutoGPT does not deviate from the right track and make the whole chain of thoughts visible to users.
得益于这组提示词,我们可以确保 ADAutoGPT 的思维逻辑不会偏离正轨,并让整个思维链对用户可见。
Question: Can you help me to know something new about Alzheimer’s Disease and maybe draw some plots for me?
问题:你能帮我了解一些关于阿尔茨海默病的新知识吗?或许还能帮我绘制一些图表?
(a) An instance of prompt specifies the format in which the AI answers questions.
(a) 提示实例规定了AI回答问题的格式。


(b) An example of AI thinking and calling functions to solve user problems
(b) AI思考并调用函数解决用户问题的示例
Fig. 2: The prompt of AD-AutoGPT, the AI assistant will answer the question based on the given format and can use the specified functions. In the prompt, tools represent the functions that AD-AutoGPT can call, including tool_ names, tool descriptions and so on.
图 2: AD-AutoGPT的提示词(prompt),AI助手将根据给定格式回答问题,并可调用指定功能。提示词中的tools代表AD-AutoGPT可调用的功能,包括tool_ names、tool描述等。
3.3 Text Summary
3.3 文本摘要
To achieve the purpose of extracting the most critical information from a large amount of news text, AD-AutoGPT performs new text summary and LDA topic modeling.
为了实现从大量新闻文本中提取最关键信息的目的,AD-AutoGPT执行了新闻文本摘要和LDA主题建模。
The text summary is mainly achieved by accessing ChatGPT or GPT4 API. Owing to the powerful text sum mari z ation ability of GPT-4, ADAutoGPT can make more efficient use of text than other models. AD-AutoGPT traverses the saved news URLs one by one, and then saves the text from the website by calling the web crawler scripts. Next, it uses ChatGPT or GPT-4 to summarize the news text. It is worth mentioning that because LLMs have a token limit, all the text here will be pre-processed first, and then be summarized. More specifically, since GPT-4 has a limit on the number of tokens, in order to summarize the complete news text, we use the map_ reduce method to process it [10].
文本摘要主要通过访问ChatGPT或GPT4 API实现。得益于GPT-4强大的文本摘要能力,ADAutoGPT能比其他模型更高效地利用文本内容。AD-AutoGPT会逐个遍历已保存的新闻URL,通过调用网络爬虫脚本保存网站文本,随后使用ChatGPT或GPT-4对新闻文本进行摘要。值得注意的是,由于大语言模型存在token限制,所有文本都会先进行预处理再进行摘要。具体而言,鉴于GPT-4存在token数量限制,为完整摘要新闻文本,我们采用map_ reduce方法进行处理 [10]。
3.4 S patio temporal Information Extraction
3.4 时空信息提取
Next, AD-AutoGPT will perform s patio temporal information extraction on the collected news articles. The temporal information can be easily extracted from news metadata while extracting place mentions from news articles is a kind of oral. Here, we adopt the geoparsing approach [45,46] which first recognizes place names from raw text, so-call toponym recognition [47,25] and then link the recognized place names to a specific geographic entity in an existing gazetteer or geospatial knowledge graphs [48,49], so-called toponym resolution [50], so that the spatial footprints (i.e., geographic coordinates) of these places can be obtained. More specifically, we use GeoText $^2$ , a pythonbased geoparsing tool to achieve this goal.
接下来,AD-AutoGPT将对收集的新闻文章进行时空信息提取。时间信息可以从新闻元数据中轻松提取,而从新闻文章中提取地点提及则属于口语化任务。为此,我们采用地理解析方法[45,46],该方法首先从原始文本中识别地名(即地名识别[47,25]),然后将识别出的地名链接到现有地名录或地理空间知识图谱[48,49]中的特定地理实体(即地名解析[50]),从而获取这些地点的空间足迹(即地理坐标)。具体而言,我们使用基于Python语言的地理解析工具GeoText$^2$来实现这一目标。
3.5 LDA Analysis
3.5 LDA分析
Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) [41] is a probabilistic topic model. LDA can give a probability distribution of topics of each document in the corpus. By analyzing a batch of document sets and extracting their topic distributions, topic clustering can be performed according to the topic distribution. LDA is a typical bag-of-words model, that is, a document is interpreted as a set of words, and there is no sequential relationship among words. In addition, a document can contain multiple topics, and each word in the document is assumed to be generated by one of the topics. LDA is an unsupervised learning method that does not require a manually labeled training set during training but only needs a document set and the total n
