CephGPT-4: An Interactive Multimodal C ep halo metric Measurement and Diagnostic System with Visual Large Language Model
CephGPT-4: 基于视觉大语言模型的交互式多模态头影测量分析与诊断系统
Lei Ma1* Jincong Han1, Zhaoxin Wang1, Dian Zhang1 School of Information Science and Technology, University of Nantong; Nantong, China, CN 226019 *Correspondence: malei@ntu.edu.cn
马雷1* 韩金聪1,王兆鑫1,张典1
南通大学信息科学技术学院;中国南通,226019
*通讯作者:malei@ntu.edu.cn
Abstract: Large-scale multimodal language models (LMMs) have achieved remarkable success in general domains. However, the exploration of diagnostic language models based on multimodal c ep halo metric medical data remains limited. In this paper, we propose a novel multimodal c ep halo metric analysis and diagnostic dialogue model. Firstly, a multimodal orthodontic medical dataset is constructed, comprising c ep halo metric images and doctor-patient dialogue data, with automatic analysis of c ep halo metric landmarks using U-net and generation of diagnostic reports. Then, the c ep halo metric dataset and generated diagnostic reports are separately fine-tuned on Minigpt-4 and VisualGLM. Results demonstrate that the CephGPT-4 model exhibits excellent performance and has the potential to revolutionize orthodontic measurement and diagnostic applications. These innovations hold revolutionary application potential in the field of orthodontics.
摘要:大规模多模态大语言模型(LMMs)在通用领域已取得显著成功,但基于头影测量(cephalometric)医学数据的诊断语言模型探索仍十分有限。本文提出了一种新型多模态头影测量分析与诊断对话模型。首先构建了包含头影测量图像与医患对话数据的多模态正畸医疗数据集,采用U-net自动分析头影测量标志点并生成诊断报告。随后分别在Minigpt-4和VisualGLM上对头影测量数据集与生成的诊断报告进行微调。结果表明,CephGPT-4模型展现出卓越性能,有望为正畸测量与诊断应用带来革命性变革。这些创新在正畸领域具有革命性的应用潜力。
Keywords: large language model, orthodontic treatment, vicuna-7b, Minigpt-4, VisualGLM
关键词:大语言模型 (Large Language Model)、正畸治疗、Vicuna-7b、MiniGPT-4、VisualGLM
1 Introduction
1 引言
Mal occlusion refers to the misalignment of teeth, abnormal dental arch relationships, and abnormal facial and jaw positioning caused by genetic or environmental factors. It is a common oral condition, with approximately $56%$ of teenagers worldwide experiencing mal occlusion issues [1]. The health of the teeth and jaws not only directly affects facial aesthetics but also impacts jaw function and oral health. Patients require orthodontic treatment to restore the aesthetic appearance and normal functionality of the oral and jaw system. C ep halo metric analysis is a method used to analyze the relationships between the skull, teeth and other bone structures. It is widely used in orthodontic clinical diagnosis, treatment planning, treatment evaluation, cr a nio facial structure research, and assessment of childhood growth and development [2]. Traditional c ep halo metric analysis involves manual annotation of anatomical landmarks on lateral X-ray images of the head. Measurements and calculations are then performed on these landmarks, including angles and distances, to analyze and assess anomalies in the anatomical structures of the oral cavity and develop treatment plans. However, traditional c ep halo metric analysis faces three major obstacles. Firstly, the calibration of anatomical landmarks requires manual annotation by clinically trained doctors, which is a time-consuming task prone to errors [3,4]. Secondly, there is an imbalance in medical resources, with overcrowding in major hospital dental departments. Patients tend to seek treatment in dental clinics for non-severe oral conditions. However, doctors and nurses in dental clinics may have limited knowledge and training, making accurate landmark annotation challenging. Lastly, providing accurate interpretation of c ep halo metric analysis results and treatment recommendations is a significant challenge. Thus, there is an urgent need for a large-scale orthodontic c ep halo metric diagnostic model to address these issues.
错颌畸形是指由遗传或环境因素导致的牙齿排列不齐、牙弓关系异常及颌面位置异常,是一种常见的口腔疾病,全球约56%的青少年存在错颌问题[1]。牙齿与颌骨的健康不仅直接影响面部美观,还会影响颌部功能与口腔健康,患者需通过正畸治疗恢复口颌系统的美观形态与正常功能。头影测量分析(cephalometric analysis)是通过分析颅骨、牙齿与其他骨骼结构关系的方法,广泛应用于正畸临床诊断、治疗方案制定、疗效评估、颅面结构研究及儿童生长发育评估[2]。传统头影测量分析需由医生在头部侧位X光片中手动标注解剖标志点,再对这些标志点进行角度、距离等测量计算,从而分析评估口腔解剖结构异常情况并制定治疗方案。但传统头影测量分析面临三大障碍:首先,解剖标志点的标定需要经过临床培训的医生手动标注,这项工作耗时且容易出错[3,4];其次,医疗资源分布不均,大型医院口腔科人满为患,轻微口腔病症患者倾向选择牙科诊所就诊,但牙科诊所医护人员的知识储备与培训可能不足,难以准确完成标志点标注;最后,如何对头影测量分析结果进行准确解读并提供治疗建议也是重大挑战。因此,亟需构建大规模的正畸头影测量诊断模型来解决这些问题。
In recent years, large language models (LLMs), represented by ChatGPT, have demonstrated remarkable performance and achieved significant success in various fields. LLMs refer to complex models trained on a massive amount of data and powerful computing resources in the field of natural language processing (NLP). These models aim to simulate human language understanding and generation abilities by learning the structure, semantics, and context of language through extensive textual data.
近年来,以ChatGPT为代表的大语言模型(LLM)展现出卓越性能,在各领域取得重大成功。大语言模型是指自然语言处理(NLP)领域中基于海量数据和强大计算资源训练出的复杂模型,旨在通过从大量文本数据中学习语言结构、语义和上下文,模拟人类语言理解与生成能力。
With the emergence of more and more large language models, innovative developments in multimodal models have been promoted. GPT-4, in particular, exhibits extraordinary performance compared to other large language models. However, detailed information about its training strategies and weight parameters is not publicly available, making it challenging for researchers to further train and fine-tune it. On the other hand, open-source large language models such as MiniGPT-4 and VisualGLM have demonstrated impressive performance in general domains, but their understanding capabilities may be insufficient in specific fields such as healthcare, hindering them from fully showcasing their true potential. Addressing the limitations of MiniGPT-4 and VisualGLM in the field of orthodontic medicine, this paper proposes the CephGPT-4 model, the world’s first Interactive Multimodal C ep halo metric Measurement and Diagnostic System with Visual Large Language Model (Fig.1).
随着越来越多大语言模型的出现,多模态模型的发展也得到了创新推动。尤其是GPT-4,相比其他大语言模型展现出非凡性能。然而其训练策略和权重参数的具体细节并未公开,这使得研究人员难以对其进行进一步训练和微调。另一方面,MiniGPT-4和VisualGLM等开源大语言模型在通用领域表现优异,但在医疗健康等特定领域的理解能力可能不足,阻碍了它们充分发挥真正潜力。针对MiniGPT-4和VisualGLM在正畸医学领域的局限性,本文提出了CephGPT-4模型,这是全球首个基于视觉大语言模型的交互式多模态头影测量诊断系统(图1)。
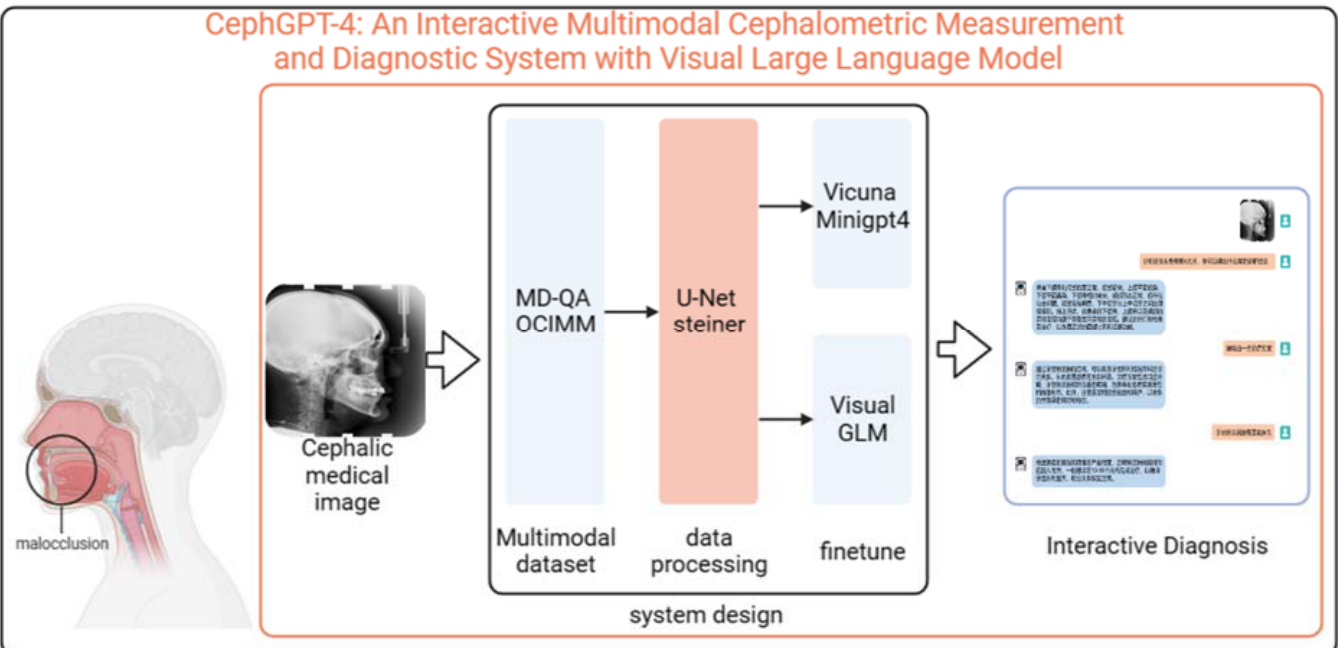

Figure 1. Illustration of CephGPT-4. CephGPT-4 incorporates a fine-tuned version of MiniGPT4 and VisualGLM on a vast collection of c ep halo metric images and doctor-patient dialogue data. With CephGPT-4, users could upload lateral X-ray images of the head are annotated with anatomical landmarks, which are used to perform measurements and calculations. These measurements include angles and distances, and they are utilized to analyze and evaluate abnormalities in the oral cavity's anatomical structures and provided treatment plans based on this analysis.
图 1: CephGPT-4 示意图。CephGPT-4 在大量头影测量图像和医患对话数据上集成了微调版 MiniGPT4 和 VisualGLM。用户可上传标注解剖标志点的头部侧位X光片,系统通过测量角度和距离来分析评估口腔解剖结构异常,并基于分析结果提供治疗方案。
2 Related Works
2 相关工作
2.1 Large Language Models
2.1 大语言模型 (Large Language Models)
Recently, researchers have discovered a model called LLaMa, which was proposed in 2021. It not only provides multiple models with parameter sizes ranging from 7 billion to 65 billion, along with detailed descriptions of their architectures and training strategies but also offers performance evaluations on various tasks [5]. Alpaca, a model based on LLaMa, demonstrates excellent performance and application potential in programming tasks through guided fine-tuning [6]. To enhance the functionality of Chinese language models, Du et al. developed a Chinese language model with 130 billion parameters using the GLM architecture, trained and fine-tuned it [7]. ChatGLM, which aligns human intentions through supervised fine-tuning, demonstrates its potential in the Chinese context [8].
最近,研究人员发现了一种名为LLaMa的模型,该模型于2021年提出。它不仅提供了参数量从70亿到650亿不等的多个模型,并详细描述了其架构和训练策略,还提供了在各种任务上的性能评估[5]。基于LLaMa的Alpaca模型通过引导微调在编程任务中展现出卓越的性能和应用潜力[6]。为增强中文语言模型的功能,Du等人利用GLM架构开发了一个1300亿参数的中文语言模型,并对其进行了训练和微调[7]。通过监督微调实现人类意图对齐的ChatGLM,展现了其在中文语境下的潜力[8]。
2.2 Pre-trained Models in Biomedical Domain
2.2 生物医学领域的预训练模型
In the field of biomedical natural language processing (NLP), several large language models derived from ChatGPT have been introduced, including ChatDoctor, Med-Alpaca, PMC-LLaMA, DoctorGLM, and Huatuo. These models are all based on the OphGLM model, which performs disease assessment and diagnosis using fundus images and incorporates ophthalmic knowledge data and real medical conversations. Furthermore, the OphGLM model integrates visual capabilities and establishes a new dataset for ophthalmic multimodal instruction following and dialogue fine-tuning. Experimental results demonstrate the outstanding performance of the OphGLM model, indicating its potential for revolutionary changes in ophthalmic clinical applications [10]. LLaVA-Med is a visual language dialogue assistant that can answer open-ended biomedical research questions related to biomedical images. By generating open-ended instruction-following data from a large-scale and widely covered biomedical image captioning dataset and applying a novel curriculum learning approach for fine-tuning a large-scale general-domain visual language model, LLaVA-Med exhibits excellent multimodal dialogue capabilities and can answer queries regarding biomedical images based on open-ended instructions. The fine-tuning results of LLaVA-Med outperform previous supervised state-ofthe-art methods on three standard biomedical visual question-answering datasets [11]. HuatuoGPT, during supervised fine-tuning, utilizes both compressed data from ChatGPT and real-world data from doctors. By training a reward model to align the language model with the strengths of both data sources, HuatuoGPT employs reinforcement learning from AI feedback (RLAIF) to enhance its performance. To evaluate and benchmark the model, a comprehensive evaluation scheme comprising automatic and manual evaluation metrics is proposed. Experimental results show that HuatuoGPT achieves state-of-the-art performance among open-source LLM models in medical consultation, particularly in GPT-4 evaluation, human evaluation, and medical benchmark datasets. Notably, the compressed language model (i.e., HuatuoGPT) outperforms its teacher model, ChatGPT, in most cases through the use of additional real-world data and RLAIF [11].
在生物医学自然语言处理(NLP)领域,已涌现出多个基于ChatGPT的大语言模型,包括ChatDoctor、Med-Alpaca、PMC-LLaMA、DoctorGLM和华佗(Huatuo)。这些模型均衍生于OphGLM模型,该模型通过眼底图像进行疾病评估与诊断,融合了眼科知识数据和真实医疗对话。此外,OphGLM整合了视觉能力,并建立了用于眼科多模态指令跟随与对话微调的新数据集。实验结果表明OphGLM具有卓越性能,预示其可能为眼科临床应用带来革命性变革[10]。LLaVA-Med是一款能回答生物医学图像相关开放性研究问题的视觉语言对话助手,通过从大规模广覆盖的生物医学图像描述数据集生成开放式指令跟随数据,并采用新颖的课程学习方法对通用领域视觉语言模型进行微调,展现出优异的多模态对话能力。LLaVA-Med在三个标准生物医学视觉问答数据集上的微调效果超越了此前最先进的监督方法[11]。华佗GPT(HuatuoGPT)在监督微调阶段同时采用ChatGPT的压缩数据和医生的真实诊疗数据,通过训练奖励模型使语言模型融合两类数据优势,并运用AI反馈强化学习(RLAIF)提升性能。为评估模型表现,研究者提出了包含自动与人工评估指标的综合评测方案。实验显示华佗GPT在医疗咨询任务中达到开源LLM模型的顶尖水平,尤其在GPT-4评估、人工评测和医疗基准数据集上表现突出。值得注意的是,通过引入额外真实数据和RLAIF技术,压缩语言模型(即华佗GPT)在多数情况下超越了其教师模型ChatGPT[11]。
XrayGPT is a novel dialogue-based medical visual language model designed to analyze and answer openended questions about chest X-rays. The model aligns a medical visual encoder (MedClip) with a fine-tuned large-scale language model (Vicuna) using a simple linear transformation. This alignment enables the model to possess excellent visual dialogue capabilities and a deep understanding of X-rays and medical domain knowledge. To improve the language model's performance in a medical context, the authors generated 217,000 interactive and high-quality summaries from free-text radiology reports to enhance the language model's performance through the fine-tuning process. This approach opens up new avenues for advancing the automated analysis of chest X-rays [12].
XrayGPT是一种新型的基于对话的医学视觉语言模型,旨在分析和回答关于胸部X射线的开放式问题。该模型通过简单的线性变换将医学视觉编码器(MedClip)与微调后的大语言模型(Vicuna)对齐。这种对齐使模型具备出色的视觉对话能力,并能深入理解X射线和医学领域知识。为了提升语言模型在医学场景下的表现,作者从自由文本放射学报告中生成了217,000份交互式高质量摘要,通过微调过程增强了语言模型的性能。这种方法为推进胸部X射线自动化分析开辟了新途径[12]。
PMC-LLaMA is an open-source language model that has been fine-tuned on a total of 4.8 million biomedical academic papers to inject medical knowledge and enhance its capabilities in the medical field. The model has undergone preliminary evaluations on three biomedical question-answering datasets, including PubMedQA, MedMCQA, and USMLE. The results show improved performance in understanding domain-specific concepts in the biomedical field and achieve high performance on question-answering benchmarks after fine-tuning [13].
PMC-LLaMA是一个开源语言模型,该模型在总计480万篇生物医学学术论文上进行了微调,以注入医学知识并增强其在医疗领域的能力。该模型已在三个生物医学问答数据集(包括PubMedQA、MedMCQA和USMLE)上进行了初步评估。结果显示其提升了对生物医学领域特定概念的理解能力,并在微调后在问答基准测试中取得了优异表现[13]。
PMC-VQA is a visual instruction fine-tuning model for medical visual question-answering (MedVQA). Efficient interpretation of critical clinical information in medical images is crucial, which is why the focus is on addressing MedVQA. First, the MedVQA questions are restructured into a generation task, which naturally follows the human-machine interaction process. A generation-based model is proposed by aligning the visual information from a pre-trained visual encoder with a large-scale language model, enabling medical visual understanding. Secondly, an extensive process is established to construct a large-scale MedVQA dataset called PMC-VQA, comprising 227,000 VQA pairs and 149,000 images, covering various modalities and diseases. The proposed model is pre-trained on PMC-VQA and fine-tuned on multiple public benchmark datasets such as VQA-RAD and SLAKE, significantly outperforming existing works. Additionally, a manually verified test set with higher challenge is introduced to evaluate the model's performance, which even the best models find difficult to solve [14].
PMC-VQA是一种用于医疗视觉问答(MedVQA)的视觉指令微调模型。高效解读医学图像中的关键临床信息至关重要,因此研究重点聚焦于解决MedVQA问题。首先,将MedVQA问题重构为生成任务,使其更符合人机交互流程。通过将预训练视觉编码器的视觉信息与大规模语言模型对齐,提出了基于生成的模型,实现了医疗视觉理解。其次,建立了一套完整的流程来构建名为PMC-VQA的大规模MedVQA数据集,包含227,000个问答对和149,000张图像,涵盖多种模态和疾病。所提模型在PMC-VQA上进行预训练,并在VQA-RAD、SLAKE等多个公开基准数据集上微调,性能显著优于现有工作。此外,还引入了人工验证的更高难度测试集来评估模型性能,该测试集即使最优模型也难以解决[14]。
3. methods
3. 方法
3.1 Dataset Construction
3.1 数据集构建
In order to improve the question-answering performance of VisualGLM and Minigpt4 in the orthodontic diagnosis dialogue task, we constructed a multimodal orthodontic medical dataset that includes doctor-patient dialogue data, orthodontic medical images, and orthodontic analysis reports.
为提高VisualGLM和Minigpt4在正畸诊断对话任务中的问答性能,我们构建了一个包含医患对话数据、正畸医学图像和正畸分析报告的多模态正畸医疗数据集。
3.1.1 Dialogue Dataset
3.1.1 对话数据集
First, we created the Medical Domain Question-Answering Dataset (MD-QA). This dataset consists of 59,642 doctor-patient dialogue records in both English and Chinese (29,624 in English and 29,618 in Chinese). The dialogues cover topics such as the interpretation of orthodontic images, diagnosis, and treatment recommendations.
首先,我们创建了医疗领域问答数据集(MD-QA)。该数据集包含59,642条中英文医患对话记录(英文29,624条,中文29,618条),涵盖正畸影像解读、诊断和治疗建议等主题。
3.1.2 Multimodal Orthodontic Cr a nio facial Imaging and Measurement Dataset
3.1.2 多模态正畸颅面成像与测量数据集
Next, we collected real clinical case samples and established the Orthodontic Cr a nio facial Imaging and Measurement Multimodal Dataset (OCIMM Dataset), which covers various types and conditions of orthodontic cr a nio facial imaging and measurement. The OCIMM Dataset includes orthodontic medical images and corresponding textual diagnostic reports.
接下来,我们收集了真实的临床病例样本,建立了正畸颅面影像与测量多模态数据集(OCIMM Dataset),涵盖各类正畸颅面影像与测量的不同类型和状况。OCIMM数据集包含正畸医学影像及相应的文本诊断报告。
The orthodontic medical images were obtained from relevant databases and image resources in the field and were annotated by professional doctors [15]. The orthodontic analysis reports were generated using an improved U-Net algorithm and the Steiner analysis method.
正畸医学图像来自该领域的相关数据库和图像资源,并由专业医生进行标注[15]。正畸分析报告采用改进的U-Net算法和Steiner分析法生成。
We designed a diagnostic neural network model for orthodontic measurements based on the U-Net architecture, which includes both local and global network models. The local network adopts a general UNet to learn local features from multiple domains, while the global network consists of parallel dilated convolutions to extract global features and address the problem of landmark point ambiguity. The method takes lateral c ep halo grams (cr a nio facial measurement analysis) as the primary input and performs measurements and analysis on multiple anatomical landmarks of the head.
我们基于U-Net架构设计了一个用于正畸测量的诊断神经网络模型,该模型包含局部和全局网络模型。局部网络采用通用UNet从多领域学习局部特征,而全局网络由并行扩张卷积组成,用于提取全局特征并解决标志点模糊问题。该方法以侧位头颅片(颅面测量分析)为主要输入,对头部的多个解剖标志点进行测量和分析。
The orthodontic analysis reports were automatically generated based on the Steiner analysis method, using a programmed calculation of angles, distances, and relationships between the landmarks. The Steiner analysis method is a measurement and analysis method for cr a nio facial imaging that was proposed by Steiner in 1953. It consists of 14 measurement parameters and was selected from previously proposed analysis methods by Riede, Downs, and others [15]. The Steiner analysis method determines the positions of the skull, teeth, and other bones based on the angles, distances, and relationships between the landmarks. It analyzes and evaluates the anomalies in the anatomical structures of the oral cavity and assesses the patient's max ill o facial morphology.
正畸分析报告基于Steiner分析法自动生成,通过编程计算标志点间的角度、距离和相互关系。Steiner分析法是1953年由Steiner提出的颅面影像测量分析方法,包含14项测量参数,其选取自Riede、Downs等人[15]先前提出的分析方法。该方法通过标志点间的角度、距离和相互关系确定颅骨、牙齿及其他骨骼的位置,分析评估口腔解剖结构异常,并评估患者颌面形态。
3.1.3 Data Cleaning
3.1.3 数据清洗
Finally, we performed data cleaning on the MD-QA and OCIMM datasets, removing low-quality images and dialogue data.
最后,我们对MD-QA和OCIMM数据集进行了数据清洗,剔除了低质量图像和对话数据。
3.2 Model Fine-tuning
3.2 模型微调
In this study, we performed fine-tuning on both MiniGPT-4 and VisualGLM models using the MD-QA and OCIMM datasets to compare their performance in the c ep halo metric analysis and diagnosis dialogue task.
在本研究中,我们使用MD-QA和OCIMM数据集对MiniGPT-4和VisualGLM模型进行了微调,以比较它们在c ep halo指标分析和诊断对话任务中的表现。
3.2.1 Fine-tuning on MiniGPT-4
3.2.1 基于 MiniGPT-4 的微调
MiniGPT-4 is an advanced fine-tuning model that combines the visual encoder BLIP-2 and the large language model Vicuna to provide novel visual language capabilities. In this process, the visual encoder and LLM (Vicuna) from BLIP-2 are frozen and aligned to jointly provide powerful functionalities.
MiniGPT-4 是一种先进的微调模型,它结合了视觉编码器 BLIP-2 和大语言模型 Vicuna,以提供新颖的视觉语言能力。在此过程中,来自 BLIP-2 的视觉编码器和 LLM (Vicuna) 被冻结并对齐,共同提供强大的功能。
First, we fine-tuned the Vicuna-7B model using a large amount of medical dialogue data from MD-QA to enable it with the ability to handle Chinese medical conversations and answer common medical questions. Then, we aligned Vicuna-7B with the visual encoder and performed fine-tuning on MiniGPT-4 using the OCIMM dataset. We employed pre-defined prompts and instruction sets to standardize the format of the training samples. This helps ensure that the model can correctly infer and answer questions given the provided instructions.
首先,我们使用MD-QA提供的大量医疗对话数据对Vicuna-7B模型进行微调,使其具备处理中文医疗对话和回答常见医学问题的能力。接着,我们将Vicuna-7B与视觉编码器对齐,并在OCIMM数据集上对MiniGPT-4进行微调。通过预定义的提示词(prompt)和指令集,我们规范了训练样本的格式,这有助于确保模型能根据给定指令正确推理并回答问题。
"###Doctor:
医生: ![]() <图像特征><指令>
<图像特征><指令>
助手:
<指令>部分分为两个部分。第一部分从预定义的指令集中随机选择指令,以确保模型能够正确响应不同形式的指令。指令集包含多种格式的指令,例如"根据这张头影测量X光片,你能提供什么诊断?"、"请从正畸医生的角度分析这张头影测量X光片"、"基于这张头影测量侧位X光片,你能提供哪些诊断建议?"等。第二部分通过添加数据集创建过程中使用的若干测量值,旨在增强模型对头影测量X光片的理解。提示格式如下(见表2)
Table 2 The format of Prompt
| Prompt (Chinese) | Prompt (Translated to English) |
| 在你作为一位口腔正畸医生的身份下,基于这张头骨 侧视X光片,你能够提供哪些医学诊断信息?\n参考 指标:SNA角:84.41,SNB角:85.7,ANB角:-1.29,Y轴 角:61.28,MP-FH角:28.03,面角:94.25,U1-NA距 离:6.34,L1-NB距离:6.6,Po-NB距离:0.08 | In your role as an orthodontist, based on this lateral cephalometric X-ray of the skull, what diagnostic information can you provide? \n Reference measurements: SNA angle: 84.41, SNB angle: 85.7, ANB angle: -1.29, Y-axis angle: 61.28, MP-FH angle: 28.03, facial angle: 94.25, U1-NA distance: 6.34, L1-NB distance: 6.6, Po-NB distance: 0.08 |
| 根据这个头骨侧面X光图片,给出你的专业诊断.\n 参考指标:SNA角:84.54,SNB角:84.27,ANB角:0.27,Y 轴角:58.64,MP-FH角:26.6,面角:89.64,U1-NA距 离:6.18,L1-NB距离:8.91,Po-NB距离:-3.56 | Based on this lateral cephalometric X-ray image of the skull, provide your professional diagnosis. nReference measurements: SNA angle: 84.54, SNB angle: 84.27, ANB angle: 0.27, Y-axis angle: 58.64, MP-FH angle: 26.6, facial angle: 89.64, U1-NA distance: 6.18, L1- NB distance: 8.91,Po-NB distance: -3.56. |
| 这是一个头骨侧面X光照片,根据它你能够提供哪些 诊断建议?\n参考指标:SNA角:80.01,SNB 角:73.87,ANB角:6.14,Y轴角:63.03,MP-FH角:31.03,面 角:96.67,U1-NA距离:0.41,L1-NB距离:11.55,Po-NB距 离:-0.94 | This is a lateral cephalometric X-ray image of the skull. Based on it, what diagnostic suggestio |
