RadLLM: A Comprehensive Healthcare Benchmark of Large Language Models for Radiology
RadLLM: 面向放射学的大语言模型综合医疗基准
Abstract
摘要
The rise of large language models (LLMs) has marked a pivotal shift in the field of natural language processing (NLP). LLMs have revolutionized a multitude of domains, and they have made a significant impact in the medical field. Large language models are now more abundant than ever, and many of these models exhibit bilingual capabilities, proficient in both English and Chinese. However, a comprehensive evaluation of these models remains to be conducted. This lack of assessment is especially apparent within the context of radiology NLP. This study seeks to bridge this gap by critically evaluating thirty two LLMs in interpreting radiology reports, a crucial component of radiology NLP. Specifically, the ability to derive impressions from radiologic findings is assessed. The outcomes of this evaluation provide key insights into the performance, strengths, and weaknesses of these LLMs, informing their practical applications within the medical domain.
大语言模型(LLM)的崛起标志着自然语言处理(NLP)领域的关键转折。这些模型已彻底改变多个领域,并在医疗行业产生重大影响。当前大语言模型数量空前,其中许多具备中英双语能力。然而针对这些模型的全面评估仍有待开展,这一缺失在放射学NLP领域尤为明显。本研究通过严格评估32个大语言模型解读放射学报告(放射学NLP的核心环节)的能力来填补这一空白,重点测试模型从影像学表现推导诊断意见的能力。评估结果揭示了这些大语言模型的性能表现、优势与不足,为其在医疗领域的实际应用提供了重要参考。
1 Introduction
1 引言
In recent years, large language models (LLMs) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] have emerged as prominent tools in the realm of natural language processing (NLP). Compared with traditional NLP models, LLMs are trained on expansive datasets and demonstrate impressive capabilities ranging from language translation to creative content generation, and problem-solving. For example, OpenAI’s dialogue model, ChatGPT $^{11}$ , has garnered widespread attention due to its outstanding performance, sparking a trend in the development of LLMs that has had profound effects on the growth of the entire AI community.
近年来,大语言模型 (LLM) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] 已成为自然语言处理 (NLP) 领域的重要工具。与传统 NLP 模型相比,大语言模型基于海量数据训练,展现出从语言翻译、创意内容生成到问题解决的卓越能力。例如 OpenAI 的对话模型 ChatGPT $^{11}$ 凭借出色表现引发广泛关注,推动了大语言模型的发展浪潮,对整个 AI 社区的发展产生了深远影响。
ChatGPT was developed based on GPT-3.5 version [9], released in November 2022. It is trained on a massive dataset of text and code and can generate text, translate languages, write different kinds of creative content, and answer your questions in an informative way. It is currently widely used in many areas, such as intelligent customer service, summary generation, and more, offering greater possibilities for applications of language models [10, 11, 1, 12]. The multimodal model GPT $4^{2}$ with 1.8 trillion parameters was released in March 2023, with overall performance and accuracy surpassing the previous version. Also, the introduction of ChatGPT plugin functionality has directly endowed ChatGPT with the ability to use other tools and connect to the internet, breaking the constraints of the model’s data. The popular rise of ChatGPT has led to a surge in the development of new LLMs. There are now several hundred open-source LLMs available, such as Hugging Face’s BLOOM [13], which is trained with 176 billion parameters across 46 natural languages and 13 programming languages while most LLMs are not publicly released and are mainly based on Latin languages with English as the main language. Also, starting from Meta’s open source LLaMA [14] series of models, researchers from Stanford University and other institutions have successively open-sourced LLaMA-based lightweight classes such as Alpaca3, Koala $\mathbf{\Sigma}^{4}$ , and Vicuna5, etc. emerged. The research and application threshold of this type of model is greatly reduced, and the training, and reasoning costs have been repeatedly reduced.
ChatGPT基于2022年11月发布的GPT-3.5版本[9]开发。该模型通过海量文本与代码数据训练,能够生成文本、翻译语言、创作多样化内容,并以信息化的方式回答问题。目前其已广泛应用于智能客服、摘要生成等多个领域,为语言模型的应用提供了更多可能性[10, 11, 1, 12]。2023年3月推出的多模态模型GPT-4$^2$拥有1.8万亿参数,整体性能与准确度超越前代。此外,ChatGPT插件功能的引入直接赋予其使用外部工具及联网能力,突破了模型数据限制。ChatGPT的流行热潮推动了大语言模型研发爆发式增长,目前已有数百个开源大语言模型,如Hugging Face推出的BLOOM[13]——该模型以1760亿参数支持46种自然语言和13种编程语言训练,但多数大语言模型未公开且主要基于拉丁语系(以英语为主)。自Meta开源LLaMA[14]系列模型后,斯坦福大学等机构研究者相继开源了基于LLaMA的轻量级模型,如Alpaca$^3$、Koala $\mathbf{\Sigma}^4$和Vicuna$^5$等。此类模型的研究应用门槛大幅降低,训练推理成本持续压缩。
Similarly, LLM ecology in other countries such as China has also begun to take shape. At present, the
同样,中国等其他国家的LLM(大语言模型)生态也已初具雏形。目前,
LLMs in China can basically be divided into three tracks: companies, institutions, and universities, such as Baidu’s ERNIE Bot $^6$ , Huawei’s Pangu models series, IDEA’s Ziya-LLaMA $7$ series, Fudan University’s MOSS $^8$ . Many corresponding models are based on LLaMA, chatGLM $^{9}$ , BLOOM, and other models that do not follow the transformer approach, such as baichuan10, RWKV [15]. These models are being used for various tasks, including natural language understanding, natural language generation, machine translation, and question answering.
中国的LLM大致可分为三个方向:企业、机构和高校,例如百度的文心一言$^6$、华为的盘古大模型系列、IDEA的Ziya-LLaMA$^7$系列、复旦大学的MOSS$^8$。许多对应模型基于LLaMA、chatGLM$^9$、BLOOM等架构,也存在不采用Transformer路线的模型,如baichuan10和RWKV [15]。这些模型正被应用于自然语言理解、自然语言生成、机器翻译和问答系统等多种任务。
The versatility of these models extends into the medical field [16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 8]. For example, LLMs can be used to generate personalized medical reports [24, 25, 26, 27], facilitate online medical consultations, remote medical diagnosis, and guidance [5, 28], and aid in medical data mining [5], among other applications. In radiology and medical image analysis, [29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39], which are fields that have been continuously intertwined with developments in AI [36, 40, 41, 42, 37, 43, 44, 45, 46], one significant application lies in the interpretation of images. Generative AI can help automate the process of preliminary diagnosis, potentially saving physicians’ time. It could be particularly useful in situations where there is a shortage of trained radiologists. Moreover, physicians may no longer need to manually enter data into the patient’s electronic medical record. In addition, these models are capable of aiding in clinical decision-making. By processing and analyzing a patient’s radiological data along with other relevant medical information, LLMs can generate patient-specific reports and provide possible diagnoses, treatment recommendations, or potential risks. Furthermore, advances in LLM have led to the development of many specialized biomedical LLMs, such as HuatuoGPT [47], an open-source model from the Chinese University of Hong Kong with the BLOOMZ [48] as backbone, uses the data distilled from ChatGPT and the real data of doctors in the supervised fine-tuning stage. And XrayGLM,11, the first Chinese multimodal large model dedicated to the diagnosis of chest X-rays, which is based on VisualGLM-6B $_ {12}$ and then fine-tuned on two open chest X-rays datasets. Others include QiZhenGPT $^{113}$ , BioMedLM $14$ , BioGPT [49], PMC-LLaMA [50], Med-PaLM [51], etc., which demonstrate significant potential of LLMs in the medical field.
这些模型的多样性延伸至医疗领域 [16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 8]。例如,大语言模型可用于生成个性化医疗报告 [24, 25, 26, 27]、辅助在线医疗咨询、远程医疗诊断与指导 [5, 28],以及助力医疗数据挖掘 [5] 等应用。在放射学和医学影像分析领域 [29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39](这些领域始终与人工智能发展紧密交织 [36, 40, 41, 42, 37, 43, 44, 45, 46]),一项重要应用在于影像解读。生成式 AI (Generative AI) 可帮助实现初步诊断流程自动化,从而节省医师时间,在缺乏专业放射科医师的情况下尤为实用。此外,医师可能不再需要手动将数据输入患者电子病历。这些模型还能辅助临床决策:通过处理分析患者的放射学数据及其他相关医疗信息,大语言模型可生成患者专属报告,并提供可能的诊断、治疗建议或潜在风险。
大语言模型的进步还催生了许多专业生物医学大模型,例如香港中文大学开源的 HuatuoGPT [47](以 BLOOMZ [48] 为架构基础),其在监督微调阶段使用了从 ChatGPT 提炼的数据和真实医生数据;以及首个专注于胸部X光诊断的中文多模态大模型 XrayGLM$_ {11}$(基于 VisualGLM-6B$_ {12}$ 架构,并在两个公开胸部X光数据集上微调)。其他代表模型包括 QiZhenGPT$^{113}$、BioMedLM$_ {14}$、BioGPT [49]、PMC-LLaMA [50]、Med-PaLM [51] 等,这些成果充分展示了大语言模型在医疗领域的巨大潜力。
Despite the escalating ubiquity of LLMs in various sectors, a comprehensive understanding and evaluation of their performance, particularly in the specialized field of radiology NLP, remains noticeably absent. This paucity of knowledge is even more stark when we consider the emerging LLMs developed in other countries such as China, a significant portion of which boast robust bilingual capabilities in both English and Chinese. Often untapped and under-evaluated, these models could offer unique advantages in processing and understanding multilingual medical data. The scarcity of in-depth, scientific performance evaluation studies on these models in the medical and radiology domains signals a significant knowledge gap that needs addressing. Given this backdrop, we believe it is paramount to undertake a rigorous and systematic exploration and analysis of these world-wide LLMs. This would not only provide a better understanding of their capabilities and limitations but also position them within the global landscape of LLMs. By comparing them with established international contenders, we aim to shed light on their relative strengths and weaknesses, providing a more nuanced understanding of the application of LLMs in the field of radiology. This, in turn, would potentially contribute to the optimization and development of more efficient and effective NLP/LLM tools for radiology.
尽管大语言模型(LLM)在各领域的应用日益普及,但对其性能的全面理解和评估,尤其是在放射学自然语言处理(NLP)这一专业领域,仍明显缺失。当我们考虑到中国等其他新兴国家开发的大语言模型时,这种认知空白更为显著——其中相当部分模型具备强大的中英双语能力。这些常被忽视且缺乏评估的模型,在处理和理解多语言医疗数据方面可能具有独特优势。医学和放射学领域缺乏对这些模型的深入科学性能评估研究,表明存在亟需填补的重要知识缺口。在此背景下,我们认为必须对这些全球范围内的大语言模型进行严格系统的探索分析。这不仅能更深入理解其能力与局限,还能明确它们在全球大语言模型格局中的定位。通过与国际知名模型的对比,我们旨在揭示其相对优劣势,从而更细致地把握大语言模型在放射学领域的应用前景。此举或将推动开发更高效、更优化的放射学NLP/大语言模型工具。
Our study is focused on the crucial aspect of radiology NLP, namely, interpreting radiology reports and deriving impressions from radiologic findings. We rigorously evaluate the selected models using a robust dataset of radiology reports, benchmarking their performance against a variety of metrics.
我们的研究聚焦于放射学自然语言处理(NLP)的关键领域,即解读放射学报告并从影像学发现中提取诊断意见。我们采用一组稳健的放射学报告数据集对选定模型进行严格评估,通过多种指标对其性能进行基准测试。
Initial findings reveal that distinct differences were observed in the models’ respective strengths and weaknesses. The implications of these findings, as well as their potential impact on the application of LLMs in radiology NLP, are discussed in detail.
初步发现表明,不同模型在各自的优势和劣势上存在显著差异。这些发现的影响,以及它们对大语言模型在放射学自然语言处理(NLP)中应用的潜在影响,将在下文详细讨论。
In the grand scheme, this study serves as a pivotal step towards the wider adoption and fine-tuning of LLMs in radiology NLP. Our observations and conclusions are aimed at spurring further research, as we firmly believe that these LLMs can be harnessed as invaluable tools for radiologists and the broader medical community.
从宏观角度看,这项研究为促进大语言模型(LLM)在放射学自然语言处理(NLP)领域的广泛应用与优化迈出了关键一步。我们的观察与结论旨在推动后续研究,因为我们坚信这些大语言模型将成为放射科医师及更广泛医疗群体的宝贵工具。
2 Related work
2 相关工作
2.1 Evaluating Large Language Models
2.1 大语言模型 (Large Language Model) 评估
The rapid development of LLMs has been revolutionizing the field of natural language processing [52, 53, 54] and domains that benefit from NLP [55, 56, 57, 58, 36, 59, 60, 28, 61, 62]. These powerful models have shown significant performance in many NLP tasks, like natural language generation (NLG) and even Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). However, utilizing these models effectively and efficiently requires a practical understanding of their capabilities and limitations, and overall performance, so evaluating these models is of paramount importance.
大语言模型(LLM)的快速发展正在彻底改变自然语言处理领域[52, 53, 54]以及受益于NLP技术的相关领域[55, 56, 57, 58, 36, 59, 60, 28, 61, 62]。这些强大模型在诸多NLP任务中展现出卓越性能,例如自然语言生成(NLG)乃至通用人工智能(AGI)。然而,要高效利用这些模型,必须切实理解其能力边界、局限性及整体表现,因此模型评估至关重要。
To compare the capabilities of different LLMs, researchers usually test with benchmark datasets in various fields (such as literature, chemistry, biology, etc.), and then evaluate their performance according to traditional indicators (such as correct answer rate, recall rate, and F1 value). The most recent study from OpenAI [63] includes the pioneering research study that assesses the performance of large language models (i.e. GPT-4) on academic and professional exams specifically crafted for educated individuals. The findings demonstrate exceptional performance of GPT-4 across a diverse array of subjects, encompassing the Uniform Bar Exam and GRE. Furthermore, an independent study conducted by Microsoft reveals that GPT-4 outperforms the USMLE, the comprehensive medical residents’ professional examination, by a significant margin [64]. Holmes et al. [65] explore the utilization of LLMs in addressing radiation oncology physics inquiries, offering insights into the scientific and medical realms. This research serves as a valuable benchmark for evaluating the performance in radiation oncology physics scenarios of LLMs.
为了比较不同大语言模型的能力,研究人员通常会在多个领域(如文学、化学、生物学等)使用基准数据集进行测试,然后根据传统指标(如正确率、召回率和F1值)评估其表现。OpenAI的最新研究[63]首次针对受过教育人群设计的学术和专业考试,评估了大语言模型(即GPT-4)的表现。研究结果表明,GPT-4在包括统一律师资格考试和GRE在内的多个学科中都展现出卓越性能。此外,Microsoft的一项独立研究表明,GPT-4在美国住院医师综合医学考试(USMLE)中的表现远超预期[64]。Holmes等人[65]探索了大语言模型在解决放射肿瘤物理问题中的应用,为科学和医学领域提供了新见解。该研究为评估大语言模型在放射肿瘤物理场景中的表现提供了重要基准。
Unlike the studies above that used traditional assessment research, Zhuang et al. [66] introduced a novel cognitive science-based [67] methodology for evaluating LLMs. Specifically, inspired by computerized adaptive testing (CAT) in psychometrics, they proposed an adaptive testing framework for evaluating LLMs that adjusts the characteristics of test items, such as difficulty level, based on the performance of individual models. They performed fine-grained diagnosis on the latest 6 instruction-tuned LLMs (i.e. ChatGPT (OpenAI), GPT-4 (OpenAI), Bard (Google), ERNIEBot (Baidu), QianWen (Alibaba), Spark (iFlytek)) and ranked them from three aspects of Subject Knowledge, Mathematical Reasoning, and Programming. The findings demonstrate a noteworthy superiority of GPT-4 over alternative models, achieving a cognitive proficiency level comparable to that of middle-level students. Similarly, traditional evaluation approaches are also not suitable for code generation tasks. Zheng et al. [68] presented a multilingual model with 13 billion parameters for code generation, and building upon HumanEval (Python only), and they developed the HumanEval-X benchmark for evaluating multilingual models by hand-writing the solutions in C++, Java, JavaScript, and Go.
与上述采用传统评估研究不同,Zhuang等人[66]提出了一种基于认知科学[67]的新方法用于评估大语言模型。具体而言,受心理测量学中计算机化自适应测试(CAT)启发,他们提出了一个自适应测试框架,可根据单个模型的表现动态调整测试项的难度等特征。研究对6个最新指令调优的大语言模型(包括ChatGPT(OpenAI)、GPT-4(OpenAI)、Bard(Google)、文心一言(百度)、通义千问(阿里巴巴)、星火(科大讯飞))进行了细粒度诊断,并从学科知识、数学推理和编程三个维度进行排名。结果显示GPT-4显著优于其他模型,其认知能力达到中等水平学生程度。传统评估方法同样不适用于代码生成任务评估。Zheng等人[68]提出了一个130亿参数的多语言代码生成模型,在HumanEval(仅支持Python语言)基础上,通过手工编写C++、Java、JavaScript和Go的解决方案,开发了用于评估多语言模型的HumanEval-X基准。
Nevertheless, a conspicuous dearth of assessment pertaining to substantial models in the realm of NLP within the domain of radiology persists. Consequently, this investigation endeavors to furnish an analytical appraisal of substantial models operating in the field of radiology. This inquiry represents the pioneering endeavor to encompass an exhaustive evaluation of large-scale language models (LLMs) within the purview of radiology, thereby serving as a catalyst for future investigations aimed at appraising the efficacy of LLMs within intricately specialized facets of medical practice.
然而,在放射学领域中针对自然语言处理(NLP)重大模型的评估仍存在显著不足。因此,本研究致力于对放射学领域运行的重大模型提供分析性评估。这项研究首次尝试对大语言模型(LLMs)在放射学范畴内进行详尽评估,从而为未来评估LLMs在高度专业化医疗实践环节中的效能研究奠定基础。
2.2 Large Language Model Development in Other Countries
2.2 其他国家的大语言模型发展
Many teams in other countries have conducted numerous attempts and research on LLMs. Examples include MOSS, developed by the OpenLMLab team at Fudan University, the BaiChuan series models developed by the Baidu team, the Sun and Moon model developed by SenseTime, PanGu developed by Huawei, ChatGLM-med developed by HIT, and YuLan-Chat developed by RUC. An introduction to these models will follow.
其他国家的许多团队对大语言模型(LLM)进行了大量尝试与研究。例如复旦大学OpenLMLab团队开发的MOSS、百度团队开发的百川系列模型、商汤科技开发的日月模型、华为开发的盘古、哈尔滨工业大学开发的ChatGLM-med,以及中国人民大学开发的玉兰-Chat。下文将对这些模型进行介绍。
MOSS [69] is an open-source series of large language models in Chinese and English, consisting of multiple versions. The base model, moss-moon-003-base, is the foundation of all MOSS versions and is pre-trained on high-quality Chinese and English corpora, encompassing 700 billion words. To adapt MOSS to dialogue scenarios, the model moss-moon-003-sft is fine-tuned on over 1.1 million rounds of dialogue data using the base model. It possesses the capabilities of instruction-following, multi-turn dialogue comprehension, and avoidance of harmful requests. Furthermore, in addition to providing consultation and question-answering functionalities, the moss-moon-003-sft-plugin model is trained not only on over 1.1 million dialogue data but also on more than 300,000 enhanced dialogue data with plugins. It extends the capabilities of the moss-moon-003-sft model to include plugin functionalities such as using search engines, generating images from text, performing calculations, and solving equations. Both moss-moon-003-sft and moss-moon-003-sft-plugin have versions with 4-bit quantization and 8-bit quantization, making them suitable for lower resource environments.
MOSS [69] 是一个开源的中英文大语言模型系列,包含多个版本。基础模型 moss-moon-003-base 是所有 MOSS 版本的基础,基于高质量中英文语料库预训练,涵盖 7000 亿词。为使 MOSS 适应对话场景,模型 moss-moon-003-sft 在基础模型上使用超过 110 万轮对话数据进行微调,具备指令跟随、多轮对话理解和规避有害请求的能力。此外,除了提供咨询和问答功能外,moss-moon-003-sft-plugin 模型不仅训练了超过 110 万条对话数据,还训练了超过 30 万条带插件的增强对话数据,扩展了 moss-moon-003-sft 模型的能力,使其包含使用搜索引擎、文生图、计算和方程求解等插件功能。moss-moon-003-sft 和 moss-moon-003-sft-plugin 均有 4 位量化和 8 位量化版本,适用于资源较低的环境。
BaiChuan, an open-source large-scale pre training language model developed by BaiChuan Intelligence, is based on the Transformers [70] architecture. It has been trained on 1.2 trillion tokens and contains 7 billion parameters, supporting both Chinese and English languages. During training, a context window length of 4096 tokens was used. In actual testing, the model can also scale to over 5000 tokens. It achieved the best performance among models of the same size on standard Chinese and English language benchmarks (C-Eval [71]/MMLU [72]).
百川 (BaiChuan) 是由百川智能开发的开源大规模预训练语言模型,基于Transformer [70] 架构。该模型在1.2万亿token上进行了训练,包含70亿参数,支持中英双语。训练时采用了4096 token的上下文窗口长度,实际测试中可扩展至5000 token以上。在标准中英文基准测试 (C-Eval [71]/MMLU [72]) 中,该模型取得了同规模模型中的最佳性能。
Chat-GLM-6B is an open bilingual language model based on the General Language Model(GLM) [73] framework, with 6.2 billion parameters. The model is trained for about 1 trillion tokens of Chinese and English corpus, supplemented by supervised fine-tuning, feedback bootstrap, and reinforcement learning with human feedback.[74] It is optimized for Chinese QA and dialogue. Furthermore, the model is capable of generating answers that align with human preference.Chat-GLM-med [75] is a variation of Chat-GLM-6B that is fine-tuned specifically for Chinese medical instructions. This Chinese medical instruction dataset is constructed using a medical knowledge graph and the GPT3.5 API. The fine-tuning process was performed on top of the existing Chat-GLM-6B model.
Chat-GLM-6B 是基于通用语言模型 (GLM) [73] 框架的开源双语大语言模型,参数量达62亿。该模型在中英文语料上训练了约1万亿token,并辅以监督微调、反馈自举和人类反馈强化学习 [74],针对中文问答和对话场景进行了优化,能够生成符合人类偏好的回答。Chat-GLM-med [75] 是 Chat-GLM-6B 的变体,专门针对中文医疗指令进行微调,其训练数据集通过医疗知识图谱和 GPT3.5 API 构建,微调过程基于现有 Chat-GLM-6B 模型完成。
YuLan [76] is developed by the GSAI team at the Renmin University of China. It utilizes the
YuLan [76] 由中国人民大学 GSAI 团队开发。它利用
LLaMA base model and is fine-tuned on a high-quality dataset of Chinese and English instructions. The dataset construction involves three stages: Open-source Instruction De duplication, Instruction Diversification based on Topic Control, and Instruction Complex if i cation. These stages aim to enhance the diversity of the instruction learning dataset.
LLaMA基础模型,并在高质量中英文指令数据集上进行微调。该数据集构建包含三个阶段:开源指令去重、基于主题控制的指令多样化以及指令复杂化。这些阶段旨在提升指令学习数据集的多样性。
There are various types of LLMs available at the current stage, and most of them are based on a base model which is a pre-trained language model following the Transformer [70] architecture. These models are further fine-tuned using domain-specific or high-quality data constructed on top of the base model. By leveraging high-quality, domain-specific data, a model with specialized knowledge can be derived from the base model.
当前阶段存在多种类型的大语言模型(LLM),其中大多数基于遵循Transformer[70]架构的预训练语言模型作为基础模型。这些模型会进一步使用在基础模型之上构建的领域专用或高质量数据进行微调。通过利用高质量的领域特定数据,可以从基础模型中衍生出具备专业知识的模型。
2.3 Applications in the Medical Field
2.3 在医疗领域的应用
The development of LLMs could result in many potential applications in the medical field. In general, they could be used in the following four areas: clinical documentation, clinical decision support, knowledge-based medical information retrieval and generation, and medical research.
大语言模型的发展可能在医疗领域带来许多潜在应用。总体而言,它们可用于以下四个领域:临床文档记录、临床决策支持、基于知识的医疗信息检索与生成,以及医学研究。
There is a large amount of clinical writing to be done by physicians and clinical professionals every day. Some can be quite laborious and time-consuming. LLMs can be possibly applied to assist in documenting patient information and symptoms [77], generating accurate and comprehensive clinical notes and test reports, and thus effectively reducing the writing load of physicians and clinical professionals. For example, an LLM summarizing the Impression from the radiology report was developed, presenting a paradigm in applications in similar domains [27].
每天,医生和临床专业人员都需要完成大量的临床文书工作,其中一些可能相当繁琐且耗时。大语言模型 (LLM) 可以用于辅助记录患者信息和症状 [77],生成准确、全面的临床笔记和检测报告,从而有效减轻医生和临床专业人员的文书负担。例如,有研究开发了一个从放射学报告中总结印象 (Impression) 部分的大语言模型 [27],为类似领域的应用提供了范例。
LLMs can also be applied to provide clinical decision support through recommending medicine usage [78], identifying appropriate imaging services from clinical presentations [79], or determining the cause of disease from numerous clinical notes and reports. When integrated with other modalities, like imaging, it can generate comprehensive information, assist physicians in disease diagnosis [80]. In addition, from cases of patients with similar symptoms, LLMs can generate patient disease outcomes, giving a prediction of what the treatment may look like, and supporting the physicians and patients make decisions on treatment options.
大语言模型还可用于提供临床决策支持,例如推荐用药 [78]、根据临床表现识别合适的影像检查服务 [79],或从大量临床记录和报告中确定病因。当与其他模态(如影像)结合时,它能生成综合信息,辅助医生进行疾病诊断 [80]。此外,基于相似症状患者案例,大语言模型可预测疾病发展结果,展示可能的治疗方案,帮助医患双方制定治疗决策。
Knowledge-based application is another place where LLMs can play a big role. For example, it could be useful to have an LLM application developed to answer health-related questions from patients [1, 81]. With the training of data in specific domains, LLM applications could provide physicians and health professionals with relevant medical information from a vast amount of scientific literature, research papers, and clinical guideline, enabling quick access to up-to-date information on disease, treatments, drug interactions, and more [3, 82]. Knowledge-based LLMs can help educate medical trainees and patients by answering generic or specific questions [83]. By integrating with a patient’s medical record, LLMs can provide personalized information and explanation of drug usage, ongoing treatment, or any relevant questions patients may have.
基于知识的应用是大语言模型可以发挥重要作用的另一个领域。例如,开发一个用于回答患者健康相关问题的LLM应用会很有价值[1, 81]。通过对特定领域数据的训练,LLM应用能够为医生和医疗专业人员从大量科学文献、研究论文和临床指南中提取相关医学信息,快速获取关于疾病、治疗方案、药物相互作用等最新资料[3, 82]。基于知识的大语言模型可以通过回答通用或特定问题来帮助培训医学生和教育患者[83]。通过与患者病历系统集成,LLM能够提供个性化的用药指导、当前治疗方案的说明,以及解答患者可能提出的任何相关问题。
LLMs can be of great benefit to the medical research community [1, 84, 85, 86, 60, 87, 88] and public health [57, 89]. For instance, the privacy of patient medical records is a big concern in clinics. The removal of identification information is mandatory before medical records used for research and results are released to the public. An LLM application help remove the identification information from medical records and could be widely utilized and beneficial to medical research [26]. Training of clinical NLP models may suffer from a lack of medical text data; augmentation of medical text data by LLMs could provide additional samples profiting the NLP model training [90]. Moreover, LLMs could conduct data collection, processing, and analysis about specific diseases, providing quantified
大语言模型 (LLM) 可为医学研究界 [1, 84, 85, 86, 60, 87, 88] 和公共卫生领域 [57, 89] 带来显著效益。例如,患者病历隐私是临床工作中的重要问题,在研究使用病历及向公众发布结果前必须去除身份识别信息。大语言模型应用能帮助去除病历中的身份信息 [26],可被广泛运用于医学研究。临床自然语言处理 (NLP) 模型的训练常面临医学文本数据不足的问题,而通过大语言模型进行医学文本数据增强能提供额外样本以提升 NLP 模型训练效果 [90]。此外,大语言模型还能针对特定疾病进行数据收集、处理和分析,提供量化...
metrics and valuable insight to researchers [91].
为研究人员提供指标和有价值的见解 [91]。
3 Methodology
3 方法
This section will discuss our testing methods for LLMs. We will begin by introducing the datasets MIMIC and OpenI, which we use for evaluation. Our testing approach involves employing a fixed set of prompts and parameters to assess the performance of LLMs in the field of radiology, specifically focusing on deriving impression-based performance from findings. To ensure consistency, we set several hyper parameters of the LLMs, namely the temperature to 0.9, the top_ k to 40, and the top_ p to 0.9. To evaluate the model’s zero-shot and few-shot performance, we utilize zero-shot, one-shot, and five-shot examples as prompts. The experimental results and their detailed analysis are presented in the results section.
本节将讨论我们针对大语言模型(LLM)的测试方法。首先介绍用于评估的数据集MIMIC和OpenI。我们的测试方法采用固定提示集和参数设置,评估大语言模型在放射学领域的表现,特别关注其根据检查结果生成印象报告的性能。为确保一致性,我们设定了大语言模型的若干超参数:温度(temperature)设为0.9,top_ k设为40,top_ p设为0.9。为评估模型的零样本(zero-shot)和少样本(few-shot)性能,我们分别采用零样本、单样本和五样本示例作为提示。实验结果及其详细分析将在结果部分呈现。
3.1 Testing Approach
3.1 测试方法
Our testing approach involves utilizing a fixed set of prompts and parameters to evaluate the LLMs. The model’s inference parameters, namely the temperature, top_ k, and top_ p, are fixed at 0.9, 40, and 0.9, respectively, to ensure consistency. We engage zero-shot, one-shot, and five-shot prompts to examine the model’s zero-shot and few-shot performance. A zero-shot prompt involves presenting the model with a new task, with no prior examples provided. A one-shot prompt involves providing the model with one prior example, while a five-shot prompt provides the model with five prior examples. This variation in prompts offers a nuanced understanding of how the LLMs operate under different conditions and degrees of prior exposure.
我们的测试方法采用固定提示词集和参数来评估大语言模型。为确保一致性,模型的推理参数(即temperature、top_ k和top_ p)分别固定为0.9、40和0.9。我们使用零样本、单样本和五样本提示来检验模型的零样本和少样本性能:零样本提示直接向模型呈现新任务且不提供示例;单样本提示提供1个示例;五样本提示则提供5个示例。这种提示词的差异化设计有助于深入理解大语言模型在不同条件和先验知识量下的运作机制。
Zero shot prompt
零样本提示
System: You are a chest radiologist that identifies the main findings and diagnosis or impression based on the given FINDINGS section of the chest X-ray report, which details the radiologists' assessment of the chest $\mathrm{X}$ -ray image. Please ensure that your response is concise and does not exceed the length of the FINDINGS. What are the main findings and diagnosis or impression based on the given Finding and the given Impression in chest X-ray report:
系统:您是一名胸部放射科医师,根据胸部X光报告中提供的FINDINGS部分识别主要发现和诊断或印象,该部分详细说明了放射科医师对胸部X光图像的评估。请确保您的回答简洁明了,且不超过FINDINGS部分的长度。基于胸部X光报告中给定的FINDINGS和IMPRESSION,主要发现和诊断或印象是什么:
One shot prompt
单次提示
System: You are a chest radiologist that identifies the main findings and diagnosis or ..
系统:你是一位胸部放射科医师,负责识别主要发现和诊断或...
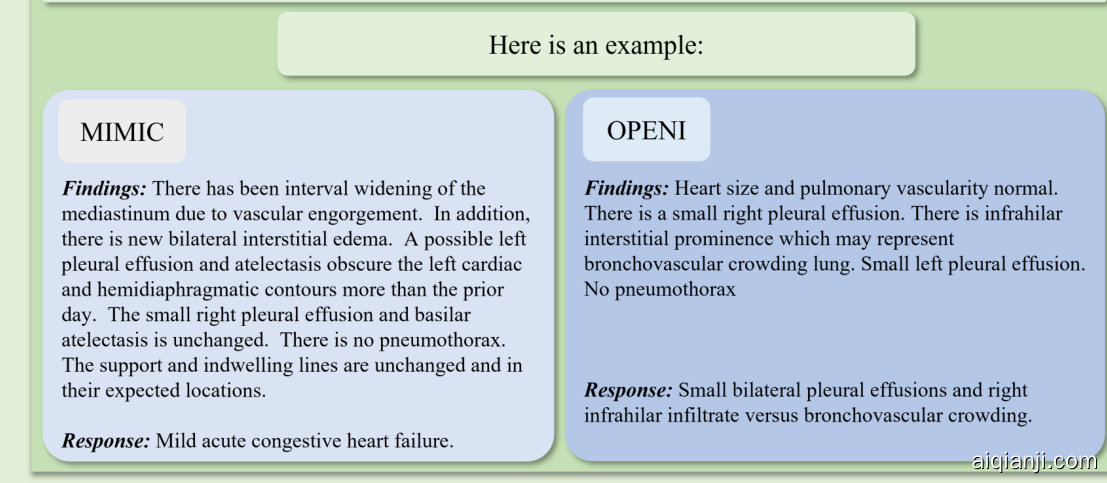
Figure 1: Zero shot prompt and one shot prompt used in the experiment.
图 1: 实验中使用的零样本提示 (zero-shot prompt) 和单样本提示 (one-shot prompt)。
Five shot prompt
五样本提示
System: You are a chest radiologist that identifies the main findings and diagnosis or ..
系统:你是一名胸部放射科医生,负责识别主要发现并给出诊断或...

Figure 2: Five shot prompt used in the experiment.
图 2: 实验中使用的五样本提示。
3.2 Model Selection
3.2 模型选择
Considering both resource constraints and the need for uniformity in model comparison, our evaluation specifically focuses on Large Language Models (LLMs) with approximately 7 billion parameters. The choice of this parameter count is based on two primary considerations. First, models of this size strike a balance between computational efficiency and model performance. They allow for faster inference, making it feasible to thoroughly evaluate the models over the complete testing dataset in a practical timeframe. Second, this parameter count is well-represented across different types of LLMs, allowing for a broad and diverse range of models to be included in the study.
考虑到资源限制和模型对比需要统一性,我们的评估特别聚焦于参数量约为70亿的大语言模型(LLM)。选择这一参数量主要基于两点考量:首先,该规模的模型在计算效率与模型性能间取得了平衡,能实现更快的推理速度,从而可在实际时间范围内对整个测试数据集进行全面评估;其次,这一参数量在不同类型的大语言模型中具有广泛代表性,使研究能涵盖多样化的模型样本。
For open-source models, we procure the necessary code and model parameters directly from their official GitHub repositories. These repositories provide comprehensive documentation and community support, ensuring that the models are implemented and evaluated correctly.
对于开源模型,我们直接从其官方GitHub仓库获取必要的代码和模型参数。这些仓库提供全面的文档和社区支持,确保模型能够被正确实现和评估。
For commercially available models, such as Sensenova, ChatGPT, GPT-4, PaLM2, and Anthropic Claude2, we utilize their respective Application Programming Interfaces (APIs). These APIs offer a structured and standardized way of interacting with the models, enabling us to input our predetermined prompts and parameters and receive the model outputs in a consistent and reliable manner.
对于市面上可用的模型,如Sensenova、ChatGPT、GPT-4、PaLM2和Anthropic Claude2,我们使用它们各自的应用程序接口(API)。这些API提供了与模型交互的结构化和标准化方式,使我们能够输入预设的提示词和参数,并以一致可靠的方式获取模型输出。
Model Summary:
模型概述:
- HuatuoGPT is a language model developed by the Shenzhen Research Institute of Big Data from the Chinese University of Hong Kong, Shenzhen. HuatuoGPT-7B is trained on the Baichuan-7B corpus, while HuatuoGPT-13B is based on Ziya-LLaMA-13B-Pretrainv1. The advantage of HuatuoGPT is in its integration of real-world medical data and the information-rich base of ChatGPT. This allows HuatuoGPT to provide detailed diagnoses and advice in medical consultation scenarios, similar to a doctor’s approach [47]. HuatuoGPT has two versions: HuatuoGPT-7B and HuatuoGPT-13B. In our experiments, we used the HuatuoGPT-7B version.
- HuatuoGPT是由香港中文大学(深圳)大数据研究院开发的大语言模型。HuatuoGPT-7B基于Baichuan-7B语料训练,HuatuoGPT-13B则基于Ziya-LLaMA-13B-Pretrainv1。该模型的优势在于融合了真实医疗数据和ChatGPT丰富的信息库,使其在医疗咨询场景中能像医生一样提供详细诊断建议[47]。HuatuoGPT包含7B和13B两个版本,本实验采用HuatuoGPT-7B版本。
- Luotuo is a Chinese language model exploited and maintained by the researchers Qiyuan Chen, Lulu Li, and Zihang Leng. Luotuo is fine-tuned by the LLaMA on Chinese corpus utilizing LoRA technique and does well in Chinese infering [92]. Luotuo has three versions: Luotuo-lora-7b-0.1, Luotuo-lora-7b-0.3, and luotuo-lora-7b-0.9. Luotuo-lora-7b-0.3 was used in the experiments.
- Luotuo 是由研究人员 Qiyuan Chen、Lulu Li 和 Zihang Leng 开发维护的中文大语言模型。该模型基于 LLaMA 架构,采用 LoRA 技术对中文语料进行微调,在中文推理任务中表现优异 [92]。目前推出三个版本:Luotuo-lora-7b-0.1、Luotuo-lora-7b-0.3 和 luotuo-lora-7b-0.9,本实验采用 Luotuo-lora-7b-0.3 版本。
- Ziya-LLaMA [93] denotes bilingual pre-trained language models based on LLaMA. It is a member of the open-source general large model series and is introduced by the Center for Cognitive Computing and Natural Language Research (CCNL) at the IDEA Research Institute. Ziya-LLaMA boasts remarkable versatility, demonstrating proficiency across a wide array of tasks including translation, programming, text classification, information extraction, summarization, copy writing, common sense Q&A, and mathematical calculation. Its comprehensive training process comprises three stages: large-scale continual pre-training, multi-task supervised fine-tuning, and human feedback learning. Ziya has four version, Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1.1, Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1, Ziya-LLaMA-7B-Reward, and Ziya-LLaMA-13B-Pretrain-v1. In this study, we investigated the Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1.
- Ziya-LLaMA [93] 是基于 LLaMA 的双语预训练语言模型。作为开源通用大模型系列的一员,该模型由IDEA研究院认知计算与自然语言研究中心(CCNL)推出。Ziya-LLaMA 具备卓越的多任务处理能力,在翻译、编程、文本分类、信息抽取、摘要生成、文案创作、常识问答和数学计算等广泛任务中均表现出色。其完整训练流程包含三个阶段:大规模持续预训练、多任务监督微调以及人类反馈学习。该系列共发布四个版本:Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1.1、Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1、Ziya-LLaMA-7B-Reward 和 Ziya-LLaMA-13B-Pretrain-v1。本研究选用的是 Ziya-LLaMA-13B-v1 版本。
- YuYan-Dialogue YuYan-Dialogue [94] is a Chinese language dialogue model by fine-tuning the YuYan-11b on a large multi-turn dialogue dataset of high quality and developed by Fuxi AI lab, Netease.Inc. It is trained on a large Chinese novel dataset of high quality and has very strong conversation generation capabilities. YuYan-Dialogue has only one version that is YuYan-Dialogue. Therefore, we used it in our experiments.
- YuYan-Dialogue
YuYan-Dialogue [94] 是由网易伏羲实验室通过在大规模高质量多轮对话数据集上微调 YuYan-11b 开发的中文对话模型。该模型基于高质量中文小说数据集训练,具备极强的对话生成能力。YuYan-Dialogue 仅有一个版本,因此我们将其用于实验。 - BenTsao BenTsao [95] is a medical language model based on LLaMA-7B model developed by SCIR Lab in Harbin Institution of Technology. It has undergone Chinese medical instruction fine-tuning and instruction tuning. They built a Chinese medical instruction dataset through the medical Knowledge graph and GPT3.5 API, based on which, they further fine-tuned the model, improving the question-and-answer effect of LLaMA in the medical field. BenTsao has four versions, LLaMA-med, LLaMA-literature, Alpaca-med, Alpaca-all-data. Here, we used the LLaMA-med (BenTsao) for comparison.
- BenTsao
BenTsao [95] 是由哈尔滨工业大学 SCIR 实验室基于 LLaMA-7B 模型开发的医疗领域大语言模型。该模型经过中文医疗指令微调 (instruction fine-tuning) 和指令优化 (instruction tuning)。研究团队通过医疗知识图谱和 GPT3.5 API 构建了中文医疗指令数据集,并在此基础上进一步微调模型,提升了 LLaMA 在医疗领域的问答效果。BenTsao 包含四个版本:LLaMA-med、LLaMA-literature、Alpaca-med 和 Alpaca-all-data。本文选用 LLaMA-med (BenTsao) 版本进行对比实验。 - XrayGLM Xray-GLM [96] is a vision-language model developed by Macao Polytechnic University. It is based on the VisualGLM-6B and fintuned on the translated Chinese version MIMIC-CXR, OpenI dataset. It has strong ability on chest Xray VQA. Here, we used the newest version of the Xray-GLM for comparison.
- XrayGLM Xray-GLM [96] 是由澳门理工大学开发的视觉语言模型。该模型基于VisualGLM-6B架构,并在翻译成中文的MIMIC-CXR和OpenI数据集上进行了微调,在胸部X光视觉问答(VQA)任务中表现优异。本次测试采用了最新版本的Xray-GLM进行对比。
- ChatGLM-Med ChatGLM-Med [75] is a language model developed by SCIR Lab in Harbin Institution of Technology. It is based on the ChatGLM-6b and has undergone Chinese medical instruction fine-tuning and instruction tuning. They built a Chinese medical instruction dataset through the medical Knowledge graph and GPT3.5 API, and on this basis, and fine-tuned the model based on the instructions of ChatGLM-6B, improving the question-and-answer effect of ChatGLM in the medical field. Here, we chose the newest version of ChatGLM-Med model for
- ChatGLM-Med
ChatGLM-Med [75] 是由哈尔滨工业大学社会计算与信息检索研究中心 (SCIR Lab) 开发的大语言模型。该模型基于 ChatGLM-6B,并进行了中文医疗指令微调和指令调优。研究团队通过医疗知识图谱和 GPT3.5 API 构建了中文医疗指令数据集,在此基础上对 ChatGLM-6B 进行指令微调,显著提升了该模型在医疗领域的问答效果。本文选用最新版 ChatGLM-Med 模型进行
comparison.
对比
- ChatGPT/GPT4 ChatGPT and GPT4 are both highly influential large language models developed by OpenAI. The full name of ChatGPT is gpt-3.5-turbo, which is developed on the basis of gpt2 and gpt3.The training process of ChatGPT mainly refers to instruct GP T [74], ChatGPT is an improved instruction GP T. The main difference from GPT-3 [9]. is that the new addition is called RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback, human feedback reinforcement learning) [97]. This training paradigm enhances human conditioning of the model output and enables a more comprehensible ranking of the results. ChatGPT has strong language understanding ability and can handle various language expressions and queries. ChatGPT has an extensive knowledge base that can answer various frequently asked questions and provide useful information. GPT-4 is a successor to GPT-3, so it may be more capable in some ways. In our experiments, we used the ChatGPT and GPT4.
- ChatGPT/GPT4
ChatGPT和GPT4都是由OpenAI开发的高影响力大语言模型。ChatGPT全称为gpt-3.5-turbo,是在gpt2和gpt3基础上开发的。ChatGPT的训练过程主要参考了instruct GPT [74],是改进版的instruct GPT。与GPT-3 [9]的主要区别在于新增了RLHF (Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback,人类反馈强化学习) [97]技术。这一训练范式增强了对模型输出的人工调控能力,并使结果排序更易理解。ChatGPT具备强大的语言理解能力,能处理各类语言表达和查询任务。其知识库覆盖广泛,可解答各类常见问题并提供实用信息。GPT-4作为GPT-3的继任者,在部分能力上表现更为突出。本实验使用了ChatGPT和GPT4。 - ChatGLM2/ChatGLM ChatGLM2 is a large language model developed by Tsinghua University, developed on the basis of the ChatGLM using the GLM framework [73]. ChatGLM2 has more powerful performance, which can handle longer contexts and perform more efficient reasoning with a more open protocol. What’s more, ChatGLM2 is an excellent bilingual pre-trained model [98]. There are many versions of ChatGLM2 depending on the size of the pattern instruction set. This work mainly tested ChatGLM2-6B and ChatGLM-6B.
- ChatGLM2/ChatGLM
ChatGLM2是由清华大学基于GLM框架[73]在ChatGLM基础上开发的大语言模型。该模型具备更强大的性能,可处理更长上下文,采用更开放的协议实现高效推理。此外,ChatGLM2是优秀的双语预训练模型[98]。根据模式指令集规模不同,ChatGLM2存在多个版本,本研究主要测试了ChatGLM2-6B和ChatGLM-6B。 - QiZhenGPT QiZhenGPT [99] is a model developed by Zhejiang University. It uses the Chinese medical instruction data set constructed by QiZhen Medical Knowledge Base, and based on this, performs instruction fine-tuning on the Chinese-LLaMA-Plus-7B, CaMA-13B, and ChatGLM-6B models. QiZhenGPT has an excellent effect in Chinese medical scenarios, and it is more accurate in answering questions than ChatGLM-6B. According to different model objects fine-tuned by instructions, QizhenGPT has three types [100]: QiZhen-ChineseLLaMA-7B, QiZhen-ChatGLM-6B, and QiZhen-CaMA-13B. In this work, we tested mainly on QiZhen-Chinese-LLaMA-7B.
- QiZhenGPT
QiZhenGPT [99] 是浙江大学开发的模型。它利用启真医学知识库构建的中文医学指令数据集,并在此基础上对 Chinese-LLaMA-Plus-7B、CaMA-13B 和 ChatGLM-6B 模型进行了指令微调。QiZhenGPT 在中文医疗场景中表现优异,其回答问题的准确性优于 ChatGLM-6B。根据指令微调的不同模型对象,启真GPT分为三种类型 [100]:QiZhen-ChineseLLaMA-7B、QiZhen-ChatGLM-6B 和 QiZhen-CaMA-13B。本工作主要测试了 QiZhen-Chinese-LLaMA-7B。 - MOSS MOSS-MOON-003 is the third version of the open-sourced plugin-augmented bilingual (i.e. Chinese and English) conversational language model MOSS, specifically from the MOSSMOON-001 to MOSS-MOON-003, developed by the OpenLMLab from Fudan University [69]. The MOSS-MOON-003-sft is fine-tuned with supervision on approximately 1.1M multi-turn conversational data to the base model, MOSS-MOON-003-base. The advantage of MOSSMOON-003 is it can follow bilingual multi-turn dialogues, refuse inappropriate requests and utilize different plugins due to its base model (i.e. MOSS-MOON-003-base was pre-trained on 700B English, Chinese, and code tokens), fine-tuning on multi-turn plugin-augmented conversational data, and further preference-aware training. There are 10 versions available: MOSS-MOON-003-base, MOSS-MOON-003-sft, MOSS-MOON-003-sft-plugin, MOSS-MOON-003-sft-int4, MOSS-MOON-003-sft-int8, MOSS-MOON-003-sft-plugin-int4, MOSS-MOON-003- sft-plugin-int8, MOSS-MOON-003-pm, MOSS-MOON-003, and MOSS-MOON-003-plugin. Inour experiments, we used the MOSS-MOON-003-sft version.
- MOSS
MOSS-MOON-003 是开源插件增强型双语(即中英文)对话语言模型 MOSS 的第三个版本,具体由复旦大学 OpenLMLab 从 MOSS-MOON-001 迭代开发至 MOSS-MOON-003 [69]。MOSS-MOON-003-sft 是在基础模型 MOSS-MOON-003-base 上使用约 110 万轮多轮对话数据进行监督微调的版本。该模型的优势在于:基于在 7000 亿个英文、中文和代码 token 上预训练的基础模型,结合多轮插件增强对话数据微调和偏好感知训练,使其能够遵循双语多轮对话、拒绝不当请求并调用不同插件。现有 10 个版本:MOSS-MOON-003-base、MOSS-MOON-003-sft、MOSS-MOON-003-sft-plugin、MOSS-MOON-003-sft-int4、MOSS-MOON-003-sft-int8、MOSS-MOON-003-sft-plugin-int4、MOSS-MOON-003-sft-plugin-int8、MOSS-MOON-003-pm、MOSS-MOON-003 和 MOSS-MOON-003-plugin。本实验采用 MOSS-MOON-003-sft 版本。 - ChatFlow ChatFlow [101] is a fully-parameterized training model developed by the Linly project team, built upon the foundations of LLaMa and Falcon and based on the TencentPretrain pre-training framework [102] and a large-scale Chinese scientific literature dataset [103]. By utilizing both Chinese and Chinese-English parallel incremental pre-training, it transfers its language capabilities from English to Chinese. The key advantage of ChatFLow is that it addresses the issue of weaker Chinese language understanding and generation abilities found in the open-source models Falcon and LLaMa. It significantly improves the encoding and generation efficiency of Chinese texts. ChatFlow comes in two versions, namely ChatFlow-7B and ChatFlow-13B. For our experiments, we utilized the ChatFlow-7B version.
- ChatFlow
ChatFlow [101] 是由Linly项目团队开发的完全参数化训练模型,基于LLaMa和Falcon架构,采用TencentPretrain预训练框架 [102] 和大规模中文科学文献数据集 [103] 构建。通过中英双语增量预训练,该模型实现了从英语到汉语的语言能力迁移。ChatFlow的核心优势在于解决了开源模型Falcon和LLaMa中文理解与生成能力较弱的问题,显著提升了中文文本的编码与生成效率。该模型提供ChatFlow-7B和ChatFlow-13B两个版本,本实验采用ChatFlow-7B版本。 - CPM-Bee CPM-Bee [104] is a large model system ecology based on OpenBMB, and it is a selfdeveloped model of the Facing Wall team. It is a completely open source, commercially available Chinese-English bilingual basic model, and it is also the second milestone achieved through the CPM-Live training process. CPM-Bee uses the Transformer auto regressive architecture, with a parameter capacity of tens of billions, pre-training on a massive corpus of trillions of tokens, and has excellent basic capabilities. There are four versions of CPM-Bee: CPM-Bee-1B, CPM-Bee-2B, CPM-Bee-5B, CPM-Bee-10B. In this experiment, we tested the performance of CPM-Bee-5B (CPM-Bee).
- CPM-Bee
CPM-Bee [104] 是基于OpenBMB的大模型系统生态,是面壁团队自研模型。作为完全开源、可商用的中英双语基础模型,它也是通过CPM-Live训练流程实现的第二个里程碑。CPM-Bee采用Transformer自回归架构,具备百亿级参数量,在万亿token规模的语料上进行预训练,拥有出色的基础能力。CPM-Bee共发布四个版本:CPM-Bee-1B、CPM-Bee-2B、CPM-Bee-5B和CPM-Bee-10B。本次实验测试了CPM-Bee-5B (CPM-Bee) 的性能表现。 - PULSE The PULSE model [105] is a large-scale language model developed on the OpenMEDLab platform. It is based on the OpenChina LLaMA 13B model, which is further fine-tuned using approximately 4,000,000 SFT data from the medical and general domains. PULSE supports a variety of natural language processing tasks in the medical field, including health education, physician exam questions, report interpretation, medical record structuring, and simulated diagnosis and treatment. PULSE has two versions, PULSE_ 7b and PULSE_ 14b. In this experiment, we tested the version of PULSE_ 7b.
- PULSE
PULSE模型 [105] 是基于OpenMEDLab平台开发的大语言模型。它以OpenChina LLaMA 13B模型为基础,通过约4,000,000条来自医疗和通用领域的SFT数据进行微调。PULSE支持医疗领域的多种自然语言处理任务,包括健康教育、医师考题、报告解读、病历结构化以及模拟诊疗。该模型拥有PULSE_ 7b和PULSE_ 14b两个版本,本实验测试的是PULSE_ 7b版本。 - Baichuan Baichuan, developed by Baichuan Intelligence, is a large pre-trained model based on the Transformer architecture. The baichuan-7B model, comprising 7 billion parameters, was trained on approximately 12 trillion tokens, utilizing the same model design as LLaMa. Subsequently, they further developed the baichuan-13B model, which is even larger in size and trained on a greater amount of data [106]. The key advantage of the Baichuan model lies in its use of an automated learning-based data weighting strategy to adjust the data distribution during training, resulting in a language model that supports both Chinese and English. It has demonstrated robust language capabilities and logical reasoning skills across various datasets. Two versions of the Baichuan model are developed: baichuan-7B and baichuan-13B. For our experiments, we utilized the baichuan-7B version.
- Baichuan
Baichuan 由百川智能开发,是基于 Transformer 架构的大型预训练模型。baichuan-7B 模型包含 70 亿参数,在约 12 万亿 Token 上训练完成,采用了与 LLaMa 相同的模型设计。随后,团队进一步开发了规模更大、训练数据量更多的 baichuan-13B 模型 [106]。该模型的核心优势在于采用基于自动学习的数据加权策略来调整训练时的数据分布,最终形成了支持中英双语的语言模型,在多种数据集上均展现出强大的语言能力和逻辑推理能力。Baichuan 开发了 baichuan-7B 和 baichuan-13B 两个版本,我们的实验采用 baichuan-7B 版本。 - AtomGPT AtomGPT [107], developed by Atom Echo, is a large language model based on the model architecture of LLaMA [108]. AtomGPT uses a large amount of Chinese and English data and codes for training, including a large number of public and non-public data sets. Developers use this method to improve model performance. AtomGPT currently has four versions: AtomGPT_ 8k, Atom GP T 14 k, Atom GP T 28 k, Atom GP T 56 k. In this experiment, we chose AtomGPT_ 8k for testing.
- AtomGPT
AtomGPT [107] 由Atom Echo开发,是基于LLaMA [108] 模型架构的大语言模型。AtomGPT使用了大量中英文数据和代码进行训练,包括众多公开和非公开数据集。开发者采用这种方法来提升模型性能。AtomGPT目前有四个版本:AtomGPT_ 8k、AtomGPT_ 14k、AtomGPT_ 28k、AtomGPT_ 56k。本实验选用AtomGPT_ 8k进行测试。 - ChatYuan ChatYuan [109] large v2 is an open-source large language model for dialogue, supports both Chinese and English languages, and in ChatGPT style. It is published by ClueAI. ChatYuan large v2 can achieve high-quality results on simple devices that allows users to operate on consumer graphics cards, PCs, and even cell phones. It got optimized for fine-tuning data, human feedback reinforcement learning, and thought chain. Also, comparing with its previous version, the model is optimized in many language abilities, like better at both Chinese and English, generating codes and so on. ChatYuan has three versions: ChatYuan-7B, ChatYuan-large-v1, ChatYuan-large-v2. In our experiments, we tested the ChatYuan-large-v2.
- ChatYuan ChatYuan [109] large v2 是一个开源的对话大语言模型,支持中英双语,采用 ChatGPT 风格。该模型由 ClueAI 发布,能在消费级显卡、PC 甚至手机等简易设备上实现高质量效果。其针对微调数据、人类反馈强化学习和思维链进行了优化。相比前代版本,该模型在多项语言能力上得到增强,例如中英文表现更优、支持代码生成等。ChatYuan 共有三个版本:ChatYuan-7B、ChatYuan-large-v1 和 ChatYuan-large-v2。本实验测试的是 ChatYuan-large-v2 版本。
- Bianque-2.0 Bianque [110] is a large model of healthcare conversations fine-tuned by a combination of directives and multiple rounds of questioning conversations. Based on BianQueCorpus, South China University of Technology chose ChatGLM-6B as the initialization model and obtained BianQue after the instruction fine-tuning training. BianQue-2.0 expands the data such as drug instruction instruction, medical encyclopedic knowledge instruction, and ChatGPT distillation instruction, which strengthens the model’s suggestion and knowledge query ability. By using Chain of Questioning, the model can relate more closely to life and to improve questioning skills, which is different from most language model. It has two versions: Bianque-1.0 and Bianque-2.0. In our experiments, we tested Bianque-2.0.
- Bianque-2.0
Bianque [110] 是通过结合指令与多轮问诊对话微调而成的医疗对话大语言模型。华南理工大学基于BianQueCorpus数据集,选择ChatGLM-6B作为初始化模型,经过指令微调训练后获得BianQue。BianQue-2.0扩展了药品说明书指令、医学百科知识指令及ChatGPT蒸馏指令等数据,增强了模型的建议与知识查询能力。通过采用问诊链 (Chain of Questioning) 技术,该模型能更贴近生活场景并提升问诊技巧,这与多数语言模型形成差异。其包含Bianque-1.0和Bianque-2.0两个版本,本实验测试的是Bianque-2.0。 - AquilaChat AquilaChat [111] is a language model developed by the Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence. AquilaChat is an SFT model based on Aquila for fine tuning and Reinforcement learning. The AquilaChat dialogue model supports smooth text dialogue and multiple language class generation tasks. By defining extensible special instruction specifications, AquilaChat can call other models and tools, and is easy to expand its functions. AquilaChat has two versions: AquilaChat-7B and AquilaChat-33B. In our experiments, we used the AquilaChat-7B version.
- AquilaChat
AquilaChat [111]是由北京智源人工智能研究院开发的大语言模型。该模型是基于Aquila进行监督微调(Supervised Fine-Tuning)和强化学习的SFT模型,支持流畅的文本对话及多语言类别生成任务。通过定义可扩展的特殊指令规范,AquilaChat能够调用其他模型和工具,并易于扩展功能。AquilaChat包含AquilaChat-7B和AquilaChat-33B两个版本,本实验采用AquilaChat-7B版本。 - Aquila Aquila [112] is a language model developed by the Beijing Academy of Artificial Intelligence. Aquila-7B is a basic model with 7 billion parameters. The Aquila basic model inherits the architectural design advantages of GPT-3, LLaMA, etc. in terms of technology, replaces a batch of more efficient low-level operator implementations, redesigns and implements the Chinese English bilingual tokenizer, upgrades the BMTrain parallel training method, and achieves nearly 8 times the training efficiency compared to Magtron+DeepSpeed Zero-2. Aquila has two versions: Aquila-7B and Aquila-33B. In our experiments, we used the Aquila -7B version.
- Aquila Aquila [112] 是由北京智源人工智能研究院开发的大语言模型。Aquila-7B 是一个拥有 70 亿参数的基础模型。Aquila 基础模型在技术上继承了 GPT-3、LLaMA 等的架构设计优势,替换了一批更高效的低层算子实现,重新设计并实现了中英双语 tokenizer,升级了 BMTrain 并行训练方法,相比 Magtron+DeepSpeed Zero-2 实现了近 8 倍的训练效率。Aquila 拥有 Aquila-7B 和 Aquila-33B 两个版本。在我们的实验中,使用了 Aquila-7B 版本。
- Chinese-Alpaca-Plus Chinese-Alpaca-Plus [100] is a language model developed by Yiming Cui etc. Chinese-Alpaca-Plus is a language model based on LLaMA. Chinese-Alpaca-Plus has improved its coding efficiency and semantic understanding of Chinese by adding 20000 Chinese tags to the existing Glossary of LLaMA [100]. Chinese-Alpaca-Plus has three versions: ChineseAlpaca-Plus-7B, Chinese-Alpaca-Plus-13B, and Chinese-Alpaca-Plus-33B. In our experiments, we used the Chinese-Alpaca-Plus-7B version.
- Chinese-Alpaca-Plus
Chinese-Alpaca-Plus [100] 是由 Yiming Cui 等人开发的大语言模型。该模型基于 LLaMA,通过在 LLaMA 原有词表基础上新增 20000 个中文 token [100],显著提升了中文编码效率和语义理解能力。Chinese-Alpaca-Plus 包含三个版本:ChineseAlpaca-Plus-7B、Chinese-Alpaca-Plus-13B 和 Chinese-Alpaca-Plus-33B。本实验采用 Chinese-Alpaca-Plus-7B 版本。 - TigerBot Tigerbot-7b-sft-v1 [113] is a language model developed by the Tigerbot Company. TigerBot-7b-sft-v1 is a large-scale language model with multiple languages and tasks. Tigerbot7b-sft-v1 is an MVP version that has undergone 3 months of closed development and over 3000 experimental iterations.Functionally, Tigerbot-7b-sft-v1 already includes the ability to generate and understand most of the classes, specifically including several major parts: content generation, image generation, open-ended Q&A, and long text interpretation.Tigerbot-7b-sft has two versions: Tigerbot-7b-sft-v1 and Tigerbot-7b-sft-v2. In our experiments, we used the tigerbot-7b-sft-v1 version.
- TigerBot
Tigerbot-7b-sft-v1 [113] 是由 Tigerbot 公司开发的大语言模型。该模型支持多语言多任务处理,是经过3个月封闭开发和超3000次实验迭代的MVP版本。功能上,Tigerbot-7b-sft-v1已具备生成和理解大多数类别内容的能力,具体涵盖四大核心模块:内容生成 (content generation) 、图像生成 (image generation) 、开放域问答 (open-ended Q&A) 以及长文本解析 (long text interpretation) 。该系列包含 Tigerbot-7b-sft-v1 和 Tigerbot-7b-sft-v2 两个版本,本实验采用 tigerbot-7b-sft-v1 版本。 - XrayPULSE XrayPULSE [114] is an extension of PULSE and made by OpenMEDLab. OpenMEDLab utilize MedCLIP as visual encoder and Q-former (BLIP2) following a
